Category:Anthropocene: Difference between revisions
Siterunner (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Siterunner (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ | ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ | ||
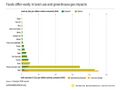
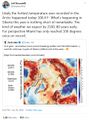
The 'Anthropocene' is a term widely used since its coining by Paul Crutzen and Eugene Stoermer in 2000 to denote the present time interval, in which many geologically significant conditions and processes are profoundly altered by human activities | The 'Anthropocene' is a term widely used since its coining by Paul Crutzen and Eugene Stoermer in 2000 to denote the present time interval, in which many geologically significant conditions and processes are profoundly altered by human activities. | ||
The 'Anthropocene' is not a formally defined geological unit within the Geological Time Scale. A proposal to formalise the 'Anthropocene' is being developed by the 'Anthropocene' Working Group for consideration by the International Commission on Stratigraphy, with a current target date of 2016 | These include changes in: | ||
*erosion and sediment transport associated with a variety of anthropogenic processes, including colonisation, agriculture, urbanisation and global warming | |||
*the chemical composition of the atmosphere, oceans and soils, with significant anthropogenic perturbations of the cycles of elements such as carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus and various metals | |||
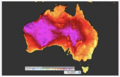
*environmental conditions generated by these perturbations; these include global warming, ocean acidification and spreading oceanic 'dead zones' | |||
*the biosphere both on land and in the sea, as a result of habitat loss, predation, species invasions and the physical and chemical changes noted above. | |||
The 'Anthropocene' is not a formally defined geological unit within the Geological Time Scale. A proposal to formalise the 'Anthropocene' is being developed by the 'Anthropocene' Working Group for consideration by the International Commission on Stratigraphy, with a current target date of 2016. | |||
The 'Anthropocene' is currently being considered by the Working Group as a potential geological epoch, i.e. at the same hierarchical level as the Pleistocene and Holocene epochs, with the implication that it is within the Quaternary Period, but that the Holocene has terminated. It might, alternatively, also be considered at a lower (Age) hierarchical level; that would imply it is a subdivision of the ongoing Holocene Epoch. | The 'Anthropocene' is currently being considered by the Working Group as a potential geological epoch, i.e. at the same hierarchical level as the Pleistocene and Holocene epochs, with the implication that it is within the Quaternary Period, but that the Holocene has terminated. It might, alternatively, also be considered at a lower (Age) hierarchical level; that would imply it is a subdivision of the ongoing Holocene Epoch. | ||
Broadly, to be accepted as a formal term the 'Anthropocene' needs to be (a) scientifically justified (i.e. the 'geological signal' currently being produced in strata now forming must be sufficiently large, clear and distinctive) and (b) useful as a formal term to the scientific community. In terms of (b), the currently informal term 'Anthropocene' has already proven to be very useful to the global change research community and thus will continue to be used, but it remains to be determined whether formalisation within the Geological Time Scale would make it more useful or broaden its usefulness to other scientific communities, such as the geological community. | Broadly, to be accepted as a formal term, the 'Anthropocene' needs to be (a) scientifically justified (i.e. the 'geological signal' currently being produced in strata now forming must be sufficiently large, clear and distinctive) and (b) useful as a formal term to the scientific community. In terms of (b), the currently informal term 'Anthropocene' has already proven to be very useful to the global change research community and thus will continue to be used, but it remains to be determined whether formalisation within the Geological Time Scale would make it more useful or broaden its usefulness to other scientific communities, such as the geological community. | ||
'''The beginning of the 'Anthropocene' is most generally considered to be at c. 1800 CE, around the beginning of the Industrial Revolution''' in Europe (Crutzen's original suggestion); other potential candidates for time boundaries have been suggested, at both earlier dates (within or even before the Holocene) or later (e.g. at the start of the nuclear age). A formal 'Anthropocene' might be defined either with reference to a particular point within a stratal section, that is, a Global Stratigraphic Section and Point (GSSP), colloquially known as a 'golden spike; or, by a designated time boundary (a Global Standard Stratigraphic Age). | |||
The | The 'Anthropocene' has emerged as a popular scientific term used by scientists, the scientifically engaged public and the media to designate '''the period of Earth's history during which humans have a decisive influence on the state, dynamics and future of the Earth system.''' | ||
It is widely agreed that the Earth is currently in this state. | |||
-- Anthropocene Working Group of the Subcommission on Quaternary Stratigraphy (International Commission on Stratigraphy) | -- Anthropocene Working Group of the Subcommission on Quaternary Stratigraphy (International Commission on Stratigraphy) | ||
Revision as of 16:00, 22 February 2016
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anthropocene
○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○
The 'Anthropocene' is a term widely used since its coining by Paul Crutzen and Eugene Stoermer in 2000 to denote the present time interval, in which many geologically significant conditions and processes are profoundly altered by human activities.
These include changes in:
- erosion and sediment transport associated with a variety of anthropogenic processes, including colonisation, agriculture, urbanisation and global warming
- the chemical composition of the atmosphere, oceans and soils, with significant anthropogenic perturbations of the cycles of elements such as carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus and various metals
- environmental conditions generated by these perturbations; these include global warming, ocean acidification and spreading oceanic 'dead zones'
- the biosphere both on land and in the sea, as a result of habitat loss, predation, species invasions and the physical and chemical changes noted above.
The 'Anthropocene' is not a formally defined geological unit within the Geological Time Scale. A proposal to formalise the 'Anthropocene' is being developed by the 'Anthropocene' Working Group for consideration by the International Commission on Stratigraphy, with a current target date of 2016.
The 'Anthropocene' is currently being considered by the Working Group as a potential geological epoch, i.e. at the same hierarchical level as the Pleistocene and Holocene epochs, with the implication that it is within the Quaternary Period, but that the Holocene has terminated. It might, alternatively, also be considered at a lower (Age) hierarchical level; that would imply it is a subdivision of the ongoing Holocene Epoch.
Broadly, to be accepted as a formal term, the 'Anthropocene' needs to be (a) scientifically justified (i.e. the 'geological signal' currently being produced in strata now forming must be sufficiently large, clear and distinctive) and (b) useful as a formal term to the scientific community. In terms of (b), the currently informal term 'Anthropocene' has already proven to be very useful to the global change research community and thus will continue to be used, but it remains to be determined whether formalisation within the Geological Time Scale would make it more useful or broaden its usefulness to other scientific communities, such as the geological community.
The beginning of the 'Anthropocene' is most generally considered to be at c. 1800 CE, around the beginning of the Industrial Revolution in Europe (Crutzen's original suggestion); other potential candidates for time boundaries have been suggested, at both earlier dates (within or even before the Holocene) or later (e.g. at the start of the nuclear age). A formal 'Anthropocene' might be defined either with reference to a particular point within a stratal section, that is, a Global Stratigraphic Section and Point (GSSP), colloquially known as a 'golden spike; or, by a designated time boundary (a Global Standard Stratigraphic Age).
The 'Anthropocene' has emerged as a popular scientific term used by scientists, the scientifically engaged public and the media to designate the period of Earth's history during which humans have a decisive influence on the state, dynamics and future of the Earth system.
It is widely agreed that the Earth is currently in this state.
-- Anthropocene Working Group of the Subcommission on Quaternary Stratigraphy (International Commission on Stratigraphy)
Subcategories
This category has the following 31 subcategories, out of 31 total.
A
C
E
G
M
N
O
P
S
Pages in category "Anthropocene"
The following 137 pages are in this category, out of 137 total.
A
B
C
- Carbon Brief
- Christianity and Climate Change Belief or Disbelief
- Clearcutting
- Climate Change - Global Warming Keyword-Terms
- Climate Change Denier Talking Points -- and Rebuttals
- Climate Conference - Paris 2015
- Climate Desk
- Climate Law Blog @Columbia Law School
- Climate migration
- Climate News
- Climate News Events Archive ... 1970 to Today
- Climate Plans Enforcement - Resources
- Climate Problems, Climate Solutions
- Copernicus EU
- Creatively Green
E
- Each of us can make a positive difference
- Earth and Space, Politics
- Earth Day
- Earth Day 2020
- Earth Day Is Every Day
- Earth Day Memories on the 50th Anniversary
- Earth Day Summit - April 22 2021
- Earth Right Now
- Earth Science Eco-Fields
- Earth Science Vital Signs
- EarthPOV
- Earthrise
- EarthTime
- Earthviews
- Earthviews from Astronauts
- Eco-nomics
- Endangered species
- Environmental agreements
- Environmental full-cost accounting
- Environmental movement
- Environmental protection
- Environmental Rules Rolled Back
- ESA Living Planet Announcement - May 2022
- Ethics and Climate Change
- European Union Green Deal - Fit for 55
- Extinction
- ExxonMobil and US House Science Committee v US Attorneys General and Environmental Groups
F
G
- Generation Green
- Genesis, Stewardship and Beyond
- Geoengineering
- George E. Brown Jr
- Glasgow Climate Summit - Pledges, Promises, Declarations - What's Next Up
- Global Climate Action Summit
- Global Forest Watch
- Going Green: Texas v. Pennsylvania
- Google Earth
- Google Earth Timelapse
- Green Education
- Green Futurist Literary Writers
- Green New Deal
- Green Politics 360
- Green Quotes
- GreenAction
- Greening Our Blue Planet
- GreenPolicy360 (eOS)
I
N
O
P
S
T
Media in category "Anthropocene"
The following 200 files are in this category, out of 1,051 total.
(previous page) (next page)- 'Thin Blue Layer' of Earth's Atmosphere 2.jpg 800 × 486; 46 KB
- 'Thin Blue Layer' of Earth's Atmosphere m.jpg 426 × 240; 15 KB
- 100 seconds to midnight.jpg 768 × 432; 30 KB
- 1977 from the Office of Science and Technology Policy.jpg 661 × 711; 177 KB
- 2015 Hottest year a.pdf ; 316 KB
- 2015 Hottest year b.pdf ; 308 KB
- 2015 temp-report s.jpg 399 × 224; 35 KB
- 2020 record temperatures.png 800 × 502; 358 KB
- 3-15-2016 10-49-38 AM.png 702 × 862; 396 KB
- 3-15-2016 12-29-07 PM.png 538 × 701; 201 KB
- 7-20-2020 GreenPolicy360 RT No.2.jpg 591 × 510; 125 KB
- A Brief History of the Future - 2s.jpg 448 × 309; 70 KB
- A Film About the Power of Protest.png 800 × 801; 715 KB
- A Flash of Green by John D. MacDonald.jpg 400 × 400; 55 KB
- A Planet Citizen View.png 799 × 1,241; 1.64 MB
- A scorching year, what about the 360 warming data.jpg 600 × 706; 106 KB
- A Stark Nuclear Warning.png 554 × 804; 171 KB
- A View of the Earth and Moon from Mars.jpg 720 × 890; 3 KB
- About Baselines and Change.png 592 × 312; 33 KB
- About the Doomsday Clock.png 361 × 415; 56 KB
- About website of The Invading Sea.png 800 × 343; 126 KB
- Above Earth .jpg 2,000 × 1,500; 278 KB
- Above.png 500 × 375; 173 KB
- Acceptance on behalf of the United States of America.png 448 × 306; 62 KB
- Act now for a livable future.png 501 × 275; 272 KB
- Acting on Climate Change.png 402 × 139; 109 KB
- Acting to make a positive difference - in St Petersburg Florida.png 600 × 723; 645 KB
- Ag production and GHG emissions.jpg 680 × 510; 33 KB
- Against the Tide - Cover - by Cornelia Dean.jpg 308 × 475; 57 KB
- Air Pollution Kills, Injures, Cripples, Disables.jpg 600 × 697; 153 KB
- Air pollution moves globally.png 620 × 412; 256 KB
- Alaska Willow - March 12 2023.png 576 × 230; 99 KB
- Alaska Willow News-March 12 2023.png 576 × 625; 235 KB
- Aldis zone blog.jpg 500 × 498; 67 KB
- All species day with homo sapien in Santa Fe .jpg 640 × 369; 98 KB
- Along Comes a Writer.png 600 × 148; 36 KB
- Amazon fires burn across the rainforest.jpg 800 × 504; 76 KB
- Andrew Wheeler confirmed to head EPA.jpg 753 × 600; 85 KB
- Another year, another record.png 800 × 294; 251 KB
- Antarctica-2018.jpg 768 × 1,024; 82 KB
- Anthropocene bks016.png 800 × 248; 227 KB
- Anthropocene Economist.png 775 × 349; 369 KB
- Anthropocene igbp globaia1.jpg 1,700 × 1,208; 4.39 MB
- Anthropocene Project-3a.png 800 × 599; 1.28 MB
- Anthropocene time.png 1,152 × 485; 892 KB
- Anthropocene-550x360.png 550 × 360; 335 KB
- Anthropocene-crutzen.jpg 628 × 347; 79 KB
- Anthropocene-the-geology-of-humanity.jpg 628 × 347; 79 KB
- Anthropocene.jpg 450 × 187; 18 KB
- Anti science, anti open data - EPA April 2017.png 429 × 616; 198 KB
- AOC re climate task force - july 8 2020.jpg 585 × 203; 38 KB
- Apocalypse When.png 505 × 398; 183 KB
- Apollo 8, Life Jan10,1969.png 480 × 635; 515 KB
- Arctic - Antarctic - Breaking.png 639 × 600; 903 KB
- Arctic 30.1 C at 62.5 N.jpg 800 × 432; 80 KB
- Arctic annual average temp 1981-2010.jpg 800 × 534; 76 KB
- Arctic drilling ban Dec 21, 2016.png 692 × 536; 119 KB
- Arctic heat in Russia-Siberia 2020.gif 784 × 408; 3.6 MB
- Arctic is in Crisis.png 800 × 432; 770 KB
- Arctic Melt - 1950-2020.png 640 × 349; 287 KB
- Arctic Sea Ice Area graphic thru 2016.png 640 × 355; 382 KB
- Arctic-100 yrs difference.jpg 640 × 883; 59 KB
- Arctic-Siberia-6-20-2020.jpg 478 × 644; 148 KB
- Arctic-swipa-spm.pdf ; 4.58 MB
- Arendt - On truth, constant lying, and results.png 590 × 800; 421 KB
- Astro POV - Mike Massimino - PlanetCitizen.png 800 × 466; 792 KB
- Astro Samantha.png 448 × 266; 78 KB
- Atmosphere Science.jpg 800 × 600; 45 KB
- Atmospheric Experiment of Humanity.jpg 519 × 574; 201 KB
- AU Too Hot.png 640 × 413; 286 KB
- Audubon - Photo by Shari McCollough.jpg 795 × 559; 76 KB
- B-21 Raider.jpg 789 × 515; 98 KB
- Backbone of Night - The Milky Way by Andrew McCarthy 2023.png 796 × 1,722; 2.3 MB
- Bad times 2020 a wordcloud via Washington Post.jpg 640 × 371; 59 KB
- Banking - finance - climate - Mann-1.jpg 452 × 640; 162 KB
- Banking - finance - climate - Mann-2.jpg 452 × 640; 164 KB
- Barrier island hubris 6-29-2021.jpg 490 × 635; 111 KB
- Be kind-2.jpg 250 × 164; 20 KB
- Ben Santer to Pruitt March 2017.png 506 × 420; 0 bytes
- Biden - clean energy ambitions.JPG 640 × 334; 31 KB
- Biden introduces leadership team - Nov 24 2020.jpg 800 × 644; 173 KB
- Biden selects Kerry as special climate envoy.jpg 592 × 505; 87 KB
- Biden urged to act - Oct 18 2021 - The Guardian.png 663 × 600; 497 KB
- Biden's assembled an all-star climate team 4-21-2021.jpg 682 × 732; 309 KB
- Biden-Harris, CNN News Online - Nov 8, 2020.jpg 800 × 484; 114 KB
- Biden-January 27 2021-Environment Day 1-News headlines.jpg 800 × 673; 122 KB
- Biden-January 27 2021-Environment Day 1.jpg 800 × 500; 80 KB
- Biden-Sanders Unity Task Force on Climate.jpg 701 × 780; 139 KB
- Big Oil Rocked by News May 27 2021.jpg 639 × 600; 84 KB
- Biggest climate related legislation in history - 1.png 800 × 188; 68 KB
- Bill McKibben switches gears-Sept 2021.jpg 518 × 265; 78 KB
- Bill McKibben to next generations.JPG 700 × 700; 203 KB
- Bill McKibben-Fate of the Earth Inaug-New School.png 800 × 735; 303 KB
- Bill Nelson on Global Temp Rise and Climate Change.png 640 × 353; 100 KB
- Bill Nye The Planet's on Fire.jpg 800 × 675; 106 KB
- Bill-Perry-is-terrified.-Why-arent-you Jan2016.png 768 × 440; 109 KB
- Biodiversity-by-dreamchaotic.jpg 600 × 173; 66 KB
- Biophysical changes forever.png 600 × 148; 15 KB
- Bloomberg Carbon Clock 10-26-2021 8-47-05 AM EST.png 800 × 195; 356 KB
- Bloomberg Live Climate Data Dashboard.jpg 640 × 756; 156 KB
- Blue atmosphere from Astro Wheelock.jpg 800 × 532; 16 KB
- Blue fragile edge thin blue line.jpg 1,200 × 798; 26 KB
- Blue Marble memories in 2022.png 768 × 969; 727 KB
- Blue Marble photo - Apollo 17.jpg 642 × 605; 129 KB
- Blue Marble photo taken by the crew of Apollo 17 (1972).jpg 642 × 605; 129 KB
- BP profit 14 yr high - Aug 2022.png 640 × 212; 63 KB
- Brazil INDC 2015.png 592 × 366; 301 KB
- Breakpoint - Reckoning with America's Environmental Crisis.jpg 329 × 500; 49 KB
- Bridenstine talks.png 1,485 × 911; 223 KB
- Buckminster and a Geodesic Dome.jpg 600 × 600; 79 KB
- Bucky Trimtab.jpg 348 × 336; 88 KB
- Bug eyes in the rainforest canopy Photo by Don Perry-2.jpg 300 × 576; 24 KB
- Bulletin from the Los Alamos Study Group - August 2022.png 800 × 561; 559 KB
- Burst of climate denial as Trump presidency ends.jpg 632 × 604; 92 KB
- C02 in atmosphere chart-3.png 570 × 800; 133 KB
- California Pipevine Swallowtail Project butterflies.png 327 × 185; 132 KB
- California's kelp forests and coastal biodiversity diminished.png 532 × 754; 307 KB
- Candle for St Francis, patron saint of ecology - 2.png 148 × 255; 51 KB
- Car heating and cooling.png 465 × 635; 261 KB
- Carbon Brief - Greenhouse gas levels 2021.png 640 × 436; 292 KB
- Carbon Clock March 23, 2017.png 800 × 194; 44 KB
- Carbon Footprint - BP-McKibben-Solnit-Aug2021.jpg 516 × 264; 66 KB
- Carbon Mapper - Launch - April 2021.jpg 800 × 323; 92 KB
- Carbon-footprint small or large.jpg 149 × 258; 0 bytes
- Carbon-footprint.jpg 297 × 516; 59 KB
- Caribbean Sea hot - June night 2024.png 676 × 600; 386 KB
- CCI-June29,2016.png 760 × 902; 201 KB
- CCS issues via Guardian opinion - July 2022.png 648 × 326; 83 KB
- CFCs then HFCs.png 800 × 382; 169 KB
- CFSV2 world temp July 3, 2023.png 600 × 800; 513 KB
- CH4 graph - 1980-2020.JPG 640 × 446; 22 KB
- Challenge of Acting for the Commons.png 700 × 548; 175 KB
- Change.jpg 800 × 473; 73 KB
- Changes in carbon dioxide per 1000 years - via Climate Central.jpg 682 × 424; 34 KB
- ChatGPT talks of fighting climate denialism.png 707 × 747; 239 KB
- China Record Heat - August 2022.png 800 × 1,343; 812 KB
- Christianity green via christian courier.jpg 768 × 512; 216 KB
- Christina Korp Earth Day and Apollo 8.jpg 519 × 264; 80 KB
- Citizens Climate Lobby - Tampa Bay.jpg 586 × 515; 125 KB
- Clean energy.png 600 × 149; 16 KB
- Cleantech is a winning issue, own it.png 600 × 283; 0 bytes
- Climate Action 25th conf in Madrid.jpg 680 × 510; 22 KB
- Climate action isn't 'bunny hugging' says Boris.jpg 800 × 264; 95 KB
- Climate action m.jpg 443 × 380; 42 KB
- Climate activist - Steven Schmidt - 1978 on.png 600 × 480; 174 KB
- Climate and National Security.jpg 603 × 533; 157 KB
- Climate Books - 2020.jpg 800 × 450; 69 KB
- Climate Central graph-800000 yrs of CO2.jpg 800 × 613; 52 KB
- Climate Central.jpg 562 × 398; 70 KB
- Climate Change Agr Nov 4, 2016.png 800 × 523; 296 KB
- Climate Change Conf Nov 6-17.png 464 × 488; 107 KB
- Climate Change COP27 - Nov 11 2022 US Representatives.jpg 712 × 444; 54 KB
- Climate Change COP27 - Nov 11 Kathy Castor.jpg 712 × 710; 77 KB
- Climate Change from Space - Climate Kit via ESA - 2022.png 800 × 421; 651 KB
- Climate change is not moving at a glacial pace.png 448 × 532; 217 KB
- Climate change unique threat to national security.png 800 × 42; 20 KB
- Climate Change US EPA.jpg 600 × 703; 95 KB
- Climate Conferences 1979-2020.jpg 768 × 768; 121 KB
- Climate course at SDG (2022) recd by Michael E Mann.png 639 × 522; 474 KB
- Climate Crisis - Emily Atkin Heated No. 1.jpg 537 × 453; 61 KB
- Climate Crisis and the Global Green New Deal.jpg 293 × 418; 33 KB
- Climate debate.jpg 493 × 580; 129 KB
- Climate Desk.jpg 390 × 226; 21 KB
- Climate diplomacy is failing - June 2020.jpg 592 × 440; 71 KB
- Climate Emergency Institute - Oct 2022.png 610 × 600; 274 KB
- Climate Emergency Institute -- 2021.jpg 800 × 450; 55 KB
- Climate emergency.jpg 800 × 450; 69 KB
- Climate Goals off course - 2018.png 800 × 556; 214 KB
- Climate Headline News around the World - July 2023.jpg 600 × 704; 151 KB
- Climate Lawsuit-Our Childrens Trust-Florida.png 462 × 760; 289 KB
- Climate Legacy of Biden.jpg 600 × 687; 265 KB
- Climate Models.png 639 × 558; 123 KB
- Climate News - Oct 28 2022.jpg 626 × 600; 88 KB
- Climate News - United Nations Report - Feb 2022.png 768 × 878; 539 KB
- Climate News Dec 4 2023 in Dubai.png 800 × 1,037; 649 KB
- Climate Plan pledges as Oct6,2015.png 529 × 409; 101 KB
- Climate Plans Enforcement - Resources - GreenPolicy.png 768 × 897; 686 KB
- Climate poll - Florida.png 640 × 267; 36 KB
- Climate Science Special Report - US - November 2017.jpg 800 × 445; 122 KB
- Climate strike - Week 171.png 739 × 600; 834 KB
- Climate Strike Around the World - Sep20,2019.jpg 700 × 830; 119 KB
- Climate Summit - Leonardo DiCaprio.png 600 × 663; 521 KB
- Climate Summit live updates - Nov 2 2021.png 751 × 600; 420 KB
- Climate Summit planned-1.jpg 800 × 301; 53 KB
- Climate Summit planned-2.jpg 800 × 187; 31 KB
- Climate Summit planned-3.jpg 800 × 278; 44 KB
- Climate Summit planned-4.jpg 800 × 241; 41 KB
- Climate usa 60 years on.jpg 800 × 480; 34 KB
- Climate365 NASA and science orgs measure and monitor.png 798 × 633; 165 KB
- ClimateNews 360.jpg 172 × 172; 9 KB
- ClimateNewsFlorida.jpg 448 × 191; 36 KB
- CO2 at Mauna Loa data - June 02, 2020 - 417.90 ppm.jpg 640 × 566; 66 KB
- CO2 cumulative emissions 1850 - 2021 - countries.jpg 640 × 462; 211 KB
- CO2 Emissions per Capita by Country 1960-2014.png 800 × 451; 424 KB
- CO2 emissions-around-the-world.png 800 × 595; 123 KB