Category:Pollution
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pollution
Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into the natural environment that cause adverse change.
Pollution can take the form of chemical substances or energy, such as noise, heat or light.
Pollutants, the components of pollution, can be either foreign substances/energies or naturally occurring contaminants. Pollution is often classed as point source or nonpoint source pollution.
Contents [hide]
1 Ancient cultures
2 Urban pollution
3 Forms of pollution --
4 Pollutants
5 Cost of pollution
6 Sources and causes
7 Effects
7.1 Human health
7.2 Environment
7.3 Environmental health information
8 Regulation and monitoring
9 Pollution control
9.1 Practices
9.2 Pollution control devices
10 Perspectives
11 Greenhouse gases and global warming
12 Most polluted places in the developing world
13 See also
14 References
15 External links
Forms of pollution
The major forms of pollution are listed below along with the particular contaminant relevant to each of them:
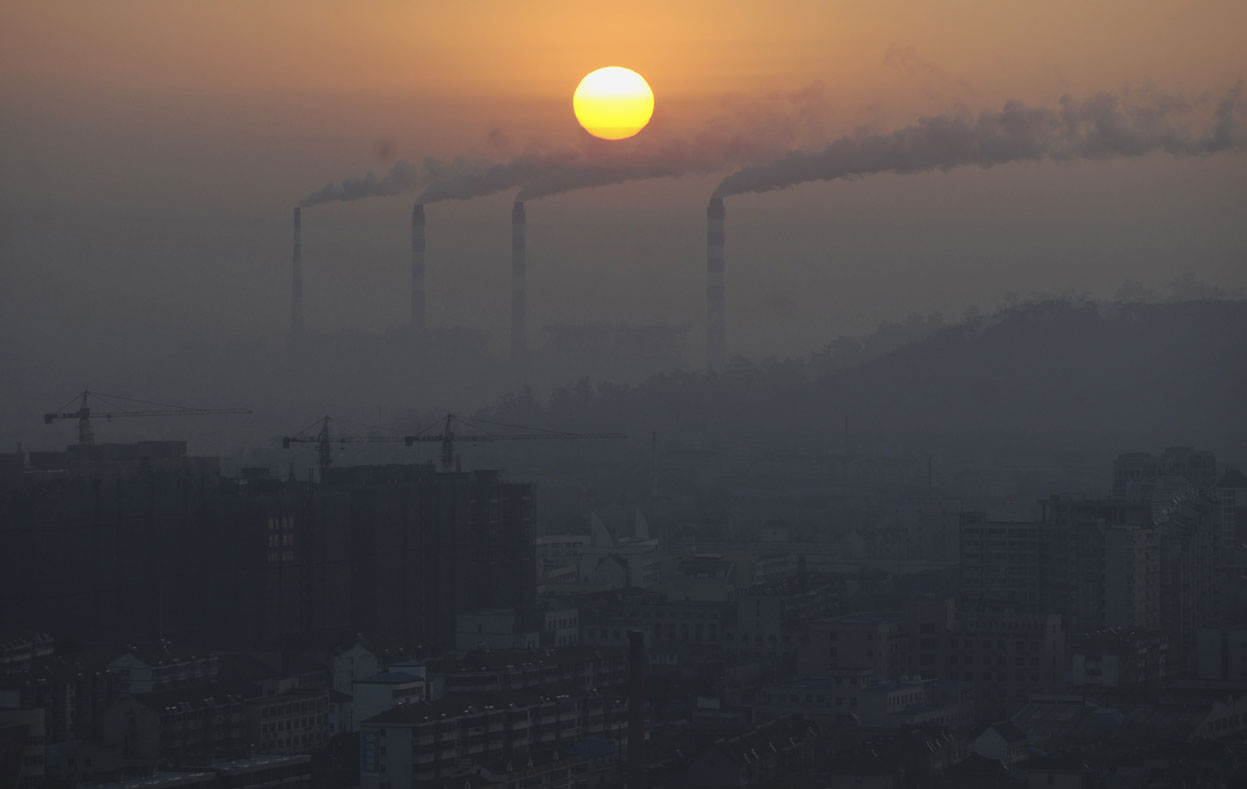
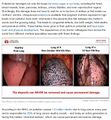
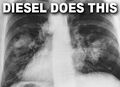
Air pollution: the release of chemicals and particulates into the atmosphere. Common gaseous pollutants include carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and nitrogen oxides produced by industry and motor vehicles. Photochemical ozone and smog are created as nitrogen oxides and hydrocarbons react to sunlight. Particulate matter, or fine dust is characterized by their micrometre size PM10 to PM2.5.
Light pollution: includes light trespass, over-illumination and astronomical interference.
Littering: the criminal throwing of inappropriate man-made objects, unremoved, onto public and private properties.
Noise pollution: which encompasses roadway noise, aircraft noise, industrial noise as well as high-intensity sonar.
Plastic pollution: involves the accumulation of plastic products in the environment that adversely affects wildlife, wildlife habitat, or humans.
Soil pollution: Soil contamination occurs when chemicals are released by spill or underground leakage. Among the significant soil contaminants are hydrocarbons, heavy metals, MTBE, herbicides, pesticides and chlorinated hydrocarbons.
Radioactive pollution:: Radioactive contamination, resulting from 20th century activities in atomic physics, such as nuclear power generation and nuclear weapons research, manufacture and deployment. (See alpha emitters and actinides in the environment.)
Thermal pollution: temperature change in natural water bodies caused by human influence, such as use of water as coolant in a power plant.
Visual pollution, which can refer to the presence of overhead power lines, motorway billboards, scarred landforms (as from strip mining), open storage of trash, municipal solid waste or space debris.
Water pollution, by the discharge of wastewater from commercial and industrial waste (intentionally or through spills) into surface waters; discharges of untreated domestic sewage, and chemical contaminants, such as chlorine, from treated sewage; release of waste and contaminants into surface runoff flowing to surface waters (including urban runoff and agricultural runoff, which may contain chemical fertilizers and pesticides); waste disposal and leaching into groundwater; eutrophication and 'littering', which has produced worldwide ocean debris .
Subcategories
This category has the following 13 subcategories, out of 13 total.
A
B
E
L
O
P
R
T
W
Pages in category "Pollution"
The following 44 pages are in this category, out of 44 total.
C
E
G
- George E. Brown Jr
- Going Green
- Google Earth Timelapse
- Green Politics 360
- Green Politics with GreenPolicy360
- Green Stories of the Day
- Green Stories of the Day - GreenPolicy360 Archive
- GreenPolicy360 Archive Highlights 2013
- GreenPolicy360 Archive Highlights 2014
- GreenPolicy360 Archive Highlights 2015
- GreenPolicy360 Archive Highlights 2016
- GreenPolicy360 Archive Highlights 2017
- GreenPolicy360 Archive Highlights 2018
- GreenPolicy360 Archive Highlights 2019
- GreenPolicy360 Archive Highlights 2020
- GreenPolicy360 Archive Highlights 2023
Media in category "Pollution"
The following 200 files are in this category, out of 202 total.
(previous page) (next page)- 1977 from the Office of Science and Technology Policy.jpg 661 × 711; 177 KB
- 3M lawsuit re forever chemicals - June 2023.png 603 × 600; 357 KB
- A scorching year, what about the 360 warming data.jpg 600 × 706; 106 KB
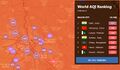
- Air Pollution - Air Quality Nov 4, 2019 Delhi.jpg 800 × 469; 92 KB
- Air Pollution Kills, Injures, Cripples, Disables.jpg 600 × 697; 153 KB
- Air pollution moves globally.png 620 × 412; 256 KB
- Alaska Willow - March 12 2023.png 576 × 230; 99 KB
- Alaska Willow News-March 12 2023.png 576 × 625; 235 KB
- Amherst-Bottle.gif 364 × 360; 35 KB
- Arctic - Kolbert - 2023.png 553 × 476; 274 KB
- BantheBag California-OutinFront.png 519 × 715; 449 KB
- Battle for Democracy.jpg 640 × 123; 24 KB
- Ben Lecomte enters the Pacific.jpg 780 × 438; 64 KB
- Biden announces EV policies - Aug 2021.jpg 600 × 604; 112 KB
- Big Wobble 2020.jpg 507 × 342; 79 KB
- Bill Nye The Planet's on Fire.jpg 800 × 675; 106 KB
- Biodegradable products--need for smarter product packaging.png 407 × 585; 34 KB
- Bloomberg Environment-water rules to change.png 800 × 429; 329 KB
- California at the forefront of US environmental policies.png 600 × 450; 50 KB
- California-Jerry Brown Sept 2016.png 640 × 291; 326 KB
- Chile's electric bus fleet.jpg 543 × 541; 74 KB
- Citizens Climate Lobby - Save Our Future Act 2021.jpg 518 × 262; 77 KB
- Climate action isn't 'bunny hugging' says Boris.jpg 800 × 264; 95 KB
- Climate cases on the rise - Nature, Sept 2021.png 800 × 562; 181 KB
- Climate Change COP27 - Nov 11 2022 US Representatives.jpg 712 × 444; 54 KB
- Climate Change COP27 - Nov 11 Kathy Castor.jpg 712 × 710; 77 KB
- Climate Change Laws - database collaboration.png 640 × 271; 76 KB
- Climate Change Laws of the World - database.PNG 768 × 845; 383 KB
- Climate Change Litigation Databases Climate Law.png 800 × 330; 73 KB
- Climate Emergency Institute - Oct 2022.png 610 × 600; 274 KB
- Climate Legacy of Biden.jpg 600 × 687; 265 KB
- Climate News - Oct 28 2022.jpg 626 × 600; 88 KB
- Climate News Dec 4 2023 in Dubai.png 800 × 1,037; 649 KB
- Climate Plans Enforcement - Resources - GreenPolicy.png 768 × 897; 686 KB
- Climate poll - Florida.png 640 × 267; 36 KB
- CO2 photo.JPG 800 × 536; 88 KB
- Congressman george.e.brown.gif 235 × 305; 41 KB
- COP27 'opening speech'.png 640 × 460; 160 KB
- COP28 News - Dec 13 2023.png 800 × 898; 410 KB
- Cradle of Civilization - and climate change.jpg 640 × 360; 70 KB
- Cradle to Cradle Products Innovation Instit.jpg 600 × 600; 72 KB
- Ddt-spray-kids-in-florida.jpg 640 × 360; 101 KB
- Disaster scenarios raise the stakes for Colorado River - 1.png 640 × 213; 56 KB
- Disaster scenarios raise the stakes for Colorado River - 2.png 640 × 154; 14 KB
- Dr Volts talks of lawns and their problems.jpg 492 × 376; 49 KB
- EarthScience Missions via the EOS - 2022.png 800 × 219; 139 KB
- EDF satellite - methane tracking.png 600 × 674; 388 KB
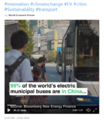
- Electric busses-China.png 492 × 569; 277 KB
- End of coal power in UK - 1.jpg 800 × 868; 112 KB
- End of coal power in UK - 2.png 800 × 557; 225 KB
- End of coal power in UK - 3.png 800 × 562; 240 KB
- End of Coal Power in UK.png 800 × 925; 739 KB
- Energy - Electric Measuring and Monitoring.png 715 × 1,978; 862 KB
- Env policy laws US 'the beginning' of env era.jpg 370 × 345; 65 KB
- Env protection on the way out Jan2018 summary.png 418 × 789; 57 KB
- Env protection on the way out Jan2018.png 582 × 522; 48 KB
- Environmental Justice and Environmental Law.jpg 274 × 668; 108 KB
- Environmental Protection Agency logo.png 380 × 414; 39 KB
- EPA .jpg 640 × 360; 15 KB
- EPA History Xin Liu-2010.pdf ; 2.88 MB
- EPA website a 'ghost page' now.png 667 × 233; 45 KB
- ERoadArlanda.png 800 × 495; 539 KB
- ESA Living Planet Symposium - Announcement.png 637 × 600; 508 KB
- ESA Living Planet Symposium - May 2022.png 700 × 600; 258 KB
- ESG Fight - Feb 2023.png 396 × 194; 88 KB
- Estuary in Clearwater on Tampa Bay.jpg 3,584 × 2,016; 1.5 MB
- Fact Checking organizations at work.jpg 800 × 390; 44 KB
- Facts about US Energy Use.jpg 697 × 600; 101 KB
- Facts Count-WaPo Reports-19127 false-misleading claims in 1226 days.jpg 601 × 489; 100 KB
- Floating adaptations - GCA - for sea-level rise - circa 2023.png 600 × 732; 273 KB
- Frackers dont clean up.jpg 591 × 493; 60 KB
- G Earth Outreach.jpg 800 × 412; 44 KB
- George Brown, Sci Com't.jpg 200 × 200; 7 KB
- Global Climate Action Summit.png 640 × 400; 470 KB
- Global Climate Change textbook-Edition2.jpg 604 × 680; 96 KB
- Global climate conferences and GHG increases.jpg 793 × 801; 56 KB
- Global Stocktake, the first GST.jpg 800 × 905; 513 KB
- Going Green 2019.jpg 800 × 356; 15 KB
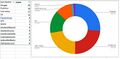
- GP360 tagcloud2 m.png 531 × 324; 132 KB
- GreenPolicy360 - May- 9-2024.png 800 × 406; 119 KB
- GreenPolicy360 - May-10-2024.png 790 × 694; 320 KB
- Haiku poems - Owl against a dusk sky - via Haiku Foundation.png 514 × 413; 144 KB
- Haikubox via RM citizen science.png 600 × 640; 466 KB
- Hansen testimony WaPo front page.jpg 480 × 210; 40 KB
- HFC Greenhouse Gas Global-Agreement-News Oct15,2016.png 974 × 768; 343 KB
- Hindu Kush-Himalayas - 2023 Report on Dangerous Climate Impacts.png 800 × 819; 1,023 KB
- Historic climate-clean energy vote in US Congress August 12 2022.jpeg 800 × 775; 384 KB
- Huge heat anomaly in 2023 - by Gavin Schmidt.png 735 × 857; 172 KB
- Hurricane-Proofing-Home-2024-Miami-Florida.png 658 × 600; 652 KB
- IEA - Support for Fossil Fuels - re 2021.jpg 559 × 800; 143 KB
- IMO Headquarters - photo via NYT.jpg 237 × 368; 22 KB
- India cities pollution.jpg 469 × 828; 100 KB
- It's time to put a price on carbon 1 m.jpg 611 × 291; 53 KB
- James Hansen 2024.jpg 600 × 658; 110 KB
- James Inhofe -- and Project 2025.png 640 × 670; 566 KB
- Jerry Brown-TW Aug21,2018.png 448 × 297; 58 KB
- Joe Biden is projected winner Nov7-2020.jpg 343 × 120; 26 KB
- Journey of a Climate Pixel - May 2022.png 800 × 399; 114 KB
- LA Times - July 2023 on the world's response to the climate crisis-1a.png 800 × 1,011; 657 KB
- LA Times on the world's response to the climate crisis-2.png 800 × 651; 297 KB
- LA Times on the world's response to the climate crisis-3.png 800 × 806; 302 KB
- LA Times on the world's response to the climate crisis-4.png 800 × 896; 321 KB
- Landsat Image Gallery.jpg 800 × 766; 187 KB
- Leah Stokes - UCSB - Prof Climate and Energy Policy.png 640 × 476; 295 KB
- Living Earth.png 441 × 183; 106 KB
- Los-angeles-smog-1970s.jpg 800 × 438; 19 KB
- Lung Care Foundation-effects of air pollution.webp.jpg 777 × 843; 303 KB
- Mapping changes in global temperature 1850-2022.png 656 × 680; 180 KB
- Mapping Our Air.png 640 × 306; 43 KB
- March for Science-1.png 800 × 291; 596 KB
- Mauna Loa-NOAA-Observatory.jpg 800 × 450; 77 KB
- Memories of Big Science advocates in the US Congress.jpg 583 × 279; 87 KB
- Methane cuts pledge - COP27.png 399 × 336; 164 KB
- Methane Reduction proposal passes in EU Parliament - May 2023.png 620 × 600; 552 KB
- MethaneSat - 1.jpg 350 × 336; 58 KB
- MethaneSat - 2.PNG 448 × 336; 172 KB
- MethaneSat - 3.PNG 448 × 303; 248 KB
- Methods to enforce climate pledges-NDCs - Dec 2021.png 539 × 480; 333 KB
- Milky Way Night Sky Black Rock Desert Nevada.jpg 731 × 1,024; 365 KB
- Monitoring Greenhouse Gases from Satellite Missions 2021-2030.png 801 × 386; 143 KB
- Montana climate trial News - 2023-08-14.png 789 × 768; 389 KB
- Montreal Protocol - effects study 2021.jpg 640 × 401; 76 KB
- Montreal Protocol update - Sept 2021.png 505 × 480; 291 KB
- Multispectral Scanning Systen - MSS.jpg 688 × 587; 103 KB
- National Climate Pledges Must Be Enforced.png 800 × 520; 122 KB
- Night skies.jpg 750 × 562; 21 KB
- No to single-use plastic.jpg 640 × 640; 63 KB
- NOAA - NCEI report on US temps 2023-2024.jpg 600 × 561; 109 KB
- NOAA extreme weather events charting.png 663 × 600; 288 KB
- NOAA report on heat records broken in US - 2023.jpg 600 × 480; 229 KB
- OaklandWastewater plant.jpg 800 × 399; 125 KB
- Ocean Pollution w Plastic-800x280.png 800 × 280; 600 KB
- Ocean Pollution w Plastic.png 1,524 × 534; 1.62 MB
- Oceans hottest in 2022.png 800 × 501; 358 KB
- Oil-Kills-4.jpg 500 × 375; 134 KB
- Our Fragile Moment.jpg 612 × 480; 80 KB
- Our Fragile Moment.png 301 × 448; 360 KB
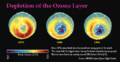
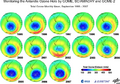
- Ozone depletion CFC's human-caused disruption.png 525 × 271; 45 KB
- Ozone depletion history nasa.jpg 500 × 428; 169 KB
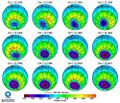
- Ozone depletion monitoring 'ozone hole' relative to CFC regulation.png 640 × 449; 331 KB
- PFAS - 1.png 640 × 335; 177 KB
- PFAS - 2.png 800 × 858; 744 KB
- Planet and plan for an Earthdata platform.png 600 × 600; 280 KB
- Planet Dove satellite image over Dubai.png 800 × 791; 1.58 MB
- Planetary-Scale Threat.jpeg 640 × 593; 101 KB
- Planetcitizens-336x336.png 336 × 336; 206 KB
- Plastic in the sand.JPG 600 × 418; 96 KB
- Plastic Reduction agr plan.png 800 × 464; 672 KB
- Pollution.jpg 720 × 480; 61 KB
- RCP-projections-damage to US economy.jpg 600 × 600; 62 KB
- Record tumble - climate change.png 727 × 333; 27 KB
- Rep. George E Brown and a young student remembering.png 640 × 325; 109 KB
- Republican Party 2024 Climate Strategy.png 589 × 344; 44 KB
- Shell lawsuit Feb 2023.png 768 × 534; 229 KB
- SMOG be gone.jpg 700 × 700; 78 KB
- SMOG in the Los Angeles basin.png 800 × 386; 413 KB
- Smog lung-damage2.jpg 460 × 246; 60 KB
- Story telling and science education.png 515 × 480; 171 KB
- Swap n Go Battery Time.jpg 460 × 302; 42 KB
- Telling stories of solutions for the climate crisis.jpg 600 × 640; 121 KB
- Temperature - SST World via Climate Change Institute - 2023 chart.png 800 × 509; 144 KB
- Temperature World - chart via Climate Change Institute.jpg 800 × 509; 67 KB
- The Climate Dictionary - as of 2023.png 600 × 727; 200 KB
- The Ocean Cleanup May2015.jpg 1,000 × 563; 39 KB
- The U.S. Role in the World ... Congressman George E Brown - 1969.jpg 448 × 334; 104 KB
- Thin Blue Layer 768x432.jpg 768 × 432; 11 KB
- Time Nov 10 2022 COP27.jpg 600 × 600; 92 KB
- Timelapse in Google Earth -1.jpg 800 × 241; 69 KB
- Timelapse in Google Earth-2.jpg 800 × 469; 151 KB
- Timelapse in Google Earth-3.jpg 372 × 556; 52 KB
- Timelapse in Google Earth-4.jpg 525 × 244; 51 KB
- Timelapse in Google Earth-5.jpg 800 × 528; 124 KB
- Timeline-climate-change-history-485-million years.jpg 800 × 276; 42 KB
- Total quits American Petroleum Institute lobby.jpg 800 × 454; 74 KB
- Toxic sky ch.jpg 1,247 × 789; 49 KB
- Tracking Biden's Environmental Record - WaPo - Feb 2021.jpg 766 × 326; 64 KB
- Tracking Biden's Environmental Record - WaPo listing - Feb 2021.jpg 588 × 397; 35 KB
- Trump promise to oil ceo gathering - 1.png 440 × 108; 19 KB
- Trump promise to oil ceo gathering - 2.png 480 × 495; 291 KB
- Trump promise to oil ceo gathering - 3.png 480 × 284; 270 KB
- Trump promise to oil ceo gathering - 4.png 480 × 480; 333 KB
- Tzoa-air quality monitoring.jpg 600 × 600; 66 KB
- UN NDC Registry - website database.png 798 × 392; 575 KB
- Update - James Hansen July 2023 'We are fools'.png 595 × 800; 610 KB
- US Election 2024 impacts our climate legacy.png 600 × 800; 719 KB
- US Public Law 95-367.png 732 × 469; 149 KB
- US Role George E Brown 2.pdf ; 151 KB
- US Role George E Brown 3.pdf ; 157 KB
- Water Pollution without sewage treatment.png 700 × 419; 602 KB
- Who really invented the climate stripes - Climate Change Education.png 600 × 600; 234 KB
- Willow project in Alaska approved.png 640 × 219; 48 KB