The Commons: Difference between revisions
Siterunner (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Siterunner (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
''[http://katharinehayhoe.com/wp2016/2015/06/05/climate-politics-and-religion/ Climate, Politics and Religion | ''[http://katharinehayhoe.com/wp2016/2015/06/05/climate-politics-and-religion/ Climate, Politics and Religion / Professor K. Hayhoe / Texas Tech / 'My opinion' - 2015]'' | ||
| |||
:······································································································ | :······································································································ | ||
Revision as of 15:29, 20 January 2020
The Challenge of Acting for the Commons
Katharine Heyhoe: At its core, climate change is a Tragedy of the Commons. First coined by Garrett Hardin in 1968, based on an 1833 publication by William Forster Lloyd, this concept dates back to the time when villages shared a common grazing area. Each individual villager would benefit from grazing as many animals as they could on the commons. If everyone did that, though, the land would become dry and barren and no one would be able to graze. As individuals, villagers lacked the incentive to limit their own behavior for the common good. Only by acting together was it possible to preserve this shared resource.
In the same way, our planet is now our global commons. Whenever we dig coal, oil, or natural gas out of the ground and burn it, we release that carbon into the atmosphere—carbon that would not naturally reach the atmosphere for millions of years.
Climate, Politics and Religion / Professor K. Hayhoe / Texas Tech / 'My opinion' - 2015
- ······································································································
- Driven by Short-term Objectives and/or Acting for the Common, Long-term Good
- Envisioning "The Commons"
- Out-in-Front Politics
New Definitions of National Security
Environment & Security: New Security Policies Beyond Nation States
Intended Nationally Determined Contributions
- ···············································································
- The Global Internet and the Commons
- Digital Citizens, Digital Rights Movement
- ·····································································
- Common Ground Values in Action
- Economics as "Eco-nomics"
- ·································································
Toward Community-wealth, Community-cooperation
- New Economics, People and the Planet | Yes Magazine: Reclaiming the Commons | Sojourner: Reclaiming the Commons
- The history of the modern environmental movement notes Mr. Alperovitz' work with Gaylord Nelson, a founder of global "Earth Day"
- ·····························································································
- Community Wealth Cities Community Wealth InfoGraphics Community Wealth Interviews Community Wealth Map Wealth Videos
- Anchor Institutions | The Cleveland Model | Community Development Corporations (CDCs) | Community Development Financial Institutions (CDFIs) | Land Trusts (CLTs) | Cooperatives (Co-ops)
- Employee Stock Ownership Plans (ESOPs) | Green Economy | Individual Wealth Building | Individual Wealth Preservation | Local Food Systems | Municipal Enterprise | New State & Local Policies | Outside the U.S. | Program Related Investments | Reclaiming the Commons
- Social Enterprise | Responsible Investing | State Asset Building Initiatives | State and Local Investments | Transit Oriented Development | University & Community Partnerships | Worker Cooperatives
···································································································
Reclaiming the Commons
The silent theft of our shared assets and civic inheritance need not continue
By David Bollier / Boston Review / Economics After Neoliberalism
• http://bostonreview.net/forum/david-bollier-reclaiming-commons
GreenPolicy360 Siterunner: This is an extended, thoughtful reflection on 'the Commons' and 'Commonwealth'. Well worth reading and sharing...
One of the great questions of contemporary American political economy is, who shall control the commons? "The commons" refers to that vast range of resources that the American people collectively own, but which are rapidly being enclosed: privatized, traded in the market, and abused...
One of the great questions of contemporary American political economy is, who shall control the commons? "The commons" refers to that vast range of resources that the American people collectively own, but which are rapidly being enclosed: privatized, traded in the market, and abused...
Varieties of Commons
The American commons comprises a wide range of shared assets and forms of community governance. Some are tangible, while others are more abstract, political, and cultural. The tangible assets of the commons include the vast quantities of oil, minerals, timber, grasslands, and other natural resources on public lands, as well as the broadcast airwaves and such public facilities as parks, stadiums, and civic institutions. The government is the trustee and steward of such resources, but "the people" are the real owners.
The commons also consists of intangible assets that are not as readily identified as belonging to the public. Such commons include the creative works and public knowledge not privatized under copyright law. This large expanse of cultural resources is sometimes known as the public domain or—as electronic networking increases its scope and intensity—"the information commons." In addition, our society has dozens of "cultural spaces" provided by communications media, public education, and nonprofit institutions. Another large realm of intangible assets consists of scientific and academic research, much of which is supported by the public through government funding. The character of these spaces changes dramatically when they are governed as markets rather than as commons.
No less important and vulnerable are what might be termed the "frontier commons": features of the natural world that have historically been too large, too small, or too elusive for any market regime to capture and that have often been regarded as parts of a common human heritage. Yet entrepreneurs and corporations are now developing ingenious ways to turn these natural commons into exploitable property. Several multinational companies are, for example, seeking to transport huge supplies of freshwater in Northern countries to "thirsty" regions in Saudi Arabia, Morocco, and southern California. Biotech companies are trying to gain proprietary control over agricultural seed-lines that have long been regarded as community assets—for example, by seeking patents for a common yellow bean grown widely in Mexico, as well as for basmati rice and neem plants in India. The human genome is a target of property claims and landowners fighting environmental regulations insist that they "own" wildlife and that the regulations amount to an unconstitutional "taking" by government.
A last category of threatened commons is that of so-called "gift economies." These are communities of shared values in which participants freely contribute time, energy, or property and over time receive benefits from membership in the community. The global corps of GNU/Linux software programmers is a prime example: enthusiasts volunteer their talents and in return receive useful rewards and group esteem For the most part, no money changes hands, yet economically valuable work occurs. Gift economies are the animating force behind scientific research communities, blood donation systems, New York City's community gardens, and Alcoholics Anonymous.
What unites these highly disparate commons—from natural resources to public domain to gift economies—is their legal and moral ownership by the American people. The commons comprises not just marketable assets, but social institutions and cultural traditions that help define our common life as Americans. In virtually every case, the market price for a resource does not begin to capture its actual value to the larger community. But generally we have no rigorous way to speak about such shared assets, or about the costs of enclosing them.
Learning to see the Commons
In an age of market triumphalism and economic myopia, it is an open question whether the notion of "commonwealth"—that we are a people with shared history, common values, and control over collectively owned assets—has practical meaning. As private interests have quietly seized the American commons, we have lost sight of our heritage as a democratic commonwealth. A society in which every human transaction is increasingly mediated by the market, in which everything is privately owned and controlled, may come to resemble a network of medieval fiefdoms, in which every minor property-holder demands tribute for the right to cross his land or ford his streams. This balkanization is bound to impede the flow of commerce and ideas—and the sustainability of innovation and democratic culture...
- ·······················································································
- Earth 'Stewardship': Religion, Community, and Values
- ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○
- ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○
Environmental Protection, Global & Indivisible
- ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○
An Earth Point of View
http://www.greenpolicy360.net/w/HelloEarth
https://www.greenpolicy360.net/w/Earth_Science_Research_from_Space
https://www.greenpolicy360.net/w/Micro-satellites
https://www.greenpolicy360.net/w/Democratization_of_Space
https://www.greenpolicy360.net/w/Earth_Imaging-New_Space
https://www.greenpolicy360.net/w/Earth_Science_Vital_Signs
http://www.greenpolicy360.net/w/Category:Earth_Observations
································································
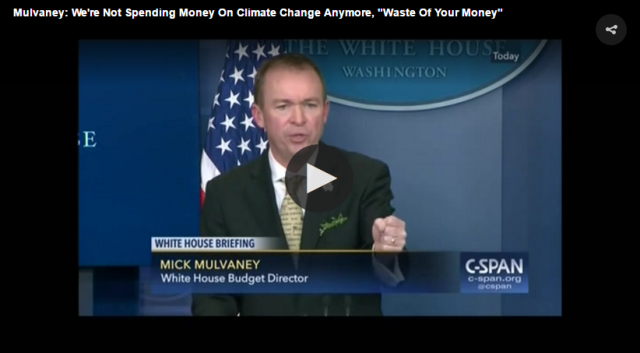
Mick Mulvaney, President Trump’s budget director:
“Regarding the question as to climate change, I think the President was fairly straightforward —
We’re not spending money on that anymore; we consider that to be a waste of your money to go out and do that.”
US Trump Doctrine: We Do Not Intend to Protect the Common Good
- ·······································································································
GreenPolicy360 & Strategic Demands: 'We Intend to Protect the Common Good'
Environmental Security & "Thin Blue"
Strategic Demands: New Definitions of National Security and Environmental Security
○
- Air Quality
- Alternative Agriculture
- Aquifers
- Anthropocene
- Atmosphere
- Atmospheric Science
- City Governments
- City-County Governments
- Clean Water
- Climate Change
- Climate Policy
- Earth
- Earth System Science
- Eco-nomics
- Ecological Economics
- Ecology Studies
- Economic Development
- Economics
- Environmental Protection
- Environmental Security
- Externalities
- EOS eco Operating System
- Food
- Forests
- Global Security
- Global Warming
- Green Best Practices
- Green Banking
- Green Business
- Green Infrastructure
- Green Politics
- Green Values
- Health
- Initiatives
- Labor Unions
- Natural Resources
- Natural Resource Economics
- New Definitions of National Security
- Networking
- New Economy
- Ocean Ecosystem
- Ocean Science
- Ocean Sustainability
- Oceans
- Permaculture
- Planet Citizen
- Planet Citizens
- Planet Scientist
- Planet Citizens, Planet Scientists
- Resilience
- Rights of Nature
- Sea-level Rise
- Sharing Economy
- Strategic Demands
- Sustainability Policies
- ThinBlueLayer
- Toxics and Pollution
- United Nations
- US Environmental Protection Agency
- Digital Citizen
- Digital Rights
- Education
- Human Rights
- Internet
- Mobile Internet
- Online Education
- Online Privacy
- Planet API
- World Wide Web