Sea-Level Rise Environmental Research Letters
Sea level rises poses greater threat to billions
March 2016
http://www.aalto.fi/en/current/news/2016-03-07-002/
More of the earth’s population lives in areas close to the sea than previously reckoned, regions that would be directly impacted by
anticipated rising in sea levels as climate change continues, according to research from Aalto University in Espoo, Finland:
These people are the most vulnerable to the rise of the sea level as well as to the increased number of floods and intensified
storms. By using new increased resolution datasets, Aalto University researchers estimate that 1.9 billion inhabitants, or 28% of the
world’s total population, live closer than 100 km from the coast in areas less than 100 meters above the present sea level.
By 2050 the amount of people in that zone is predicted to increase to 2.4 billion, while population living lower than 5 meters
will reach 500 million people. Many of these people need to adapt their livelihoods to changing climate, say Assistant Professor Matti
Kummu from Aalto University.
The study found that while population and wealth concentrate by the sea, food must be grown further and further away from where
people live. Highlands and mountain areas are increasingly important from food production point of view, but also very vulnerable to
changes in climate.
Over the past century there has been a clear tendency that cropland and pasture areas have grown most in areas outside the
population hotspots, and decreased in coastal areas. This will most probably only continue in the future, summarises Professor Olli Varis
from Aalto University.
Even though people and wealth continue to accumulate in coastal proximity, their growth is even faster in inland and mountainous
areas, the study reveals. This contradicts the existing studies. In the future, the world will be less diverse in terms of urbanisation
and economic output, when assessing it from geospatial point of view.
For the analysis, researchers used several global gridded datasets. They first created a geographic zoning in relation to the
elevation and proximity to coast. This was then used to study the factors included in the study, which were grouped into five clusters:
climate, population, agriculture, economy, and impact on environment. For the factors with temporal extent, the researchers also assessed
their development over time period of 1900-2050.
The study was made in collaboration with researchers from Aalto University, Finland, the Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam, Netherlands,
National Institute for Statistics, Italy, and University of Zurich, Switzerland.
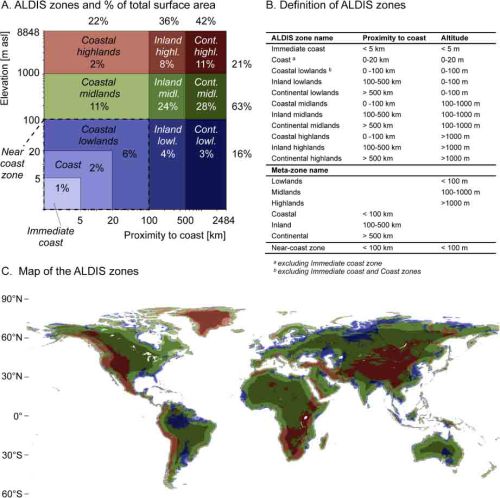
Here’s the basis for their findings, a global mapping based on Altitude and Distance to the Sea [ALDIS] zones:
Overview of the geographic zones.
- (A) The ALDIS zoning and the share of the global land surface area in each zone (note the logarithmic scale on both axes);
- (B) definition of ALDIS zones and meta-zones; and
- (C) map of the ALDIS zones (colours correspond to the ones in (A)-tile).
The full report has been published as a rare open [free] access article by Environmental Research Letters.
Article PDF - http://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1748-9326/11/3/034010/pdf
- Antarctica
- Antigua and Barbuda
- Anthropocene
- Aquifers
- Bahamas
- Barbados
- Belize
- Cabo Verde
- Caribbean
- Climate Policy
- Comoros
- Cook Islands
- Cuba
- Divestment from Fossil Fuels
- Dominica
- Dominican Republic
- Earth
- Earth Science
- Earth Science from Space
- Ecology Studies
- Environmental Protection
- Environmental Security
- Fiji
- Global Security
- Grenada
- Guinea-Bissau
- Guyana
- Haiti
- Kiribati
- Jamaica
- Maldives
- Marshall Islands
- Micronesia
- Nauru
- New Zealand
- Niue
- Oceania
- Palau
- Papua New Guinea
- Samoa
- Saint Kitts and Nevis
- Saint Lucia
- Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
- Sao Tome and Principe
- Seychelles
- Small Island Developing States
- Singapore
- Solomon Islands
- Climate Change
- Cryosphere
- Earth Imaging
- Earth Observations
- Environmental Security, National Security
- Ocean Ecosystem
- Oceans
- Ocean Science
- Planet Citizen
- Planet Scientist
- Sea-level Rise
- Atmospheric Science
- Earth360
- ESA
- Green Politics
- NASA
- Planet Citizens, Planet Scientists
- Resilience
- Sustainability
- Sustainability Policies
- US Environmental Protection Agency
- Sea-Level Rise & Mitigation
- Whole Earth