Category:Internet: Difference between revisions
Siterunner (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Siterunner (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<addthis /> | <addthis /> | ||
| Line 4: | Line 5: | ||
[[File:Digital Rights Tag Cloud from GreenPolicy360.net.png]] | [[File:Digital Rights Tag Cloud from GreenPolicy360.net.png]] | ||
<big><big><big><big>Internet</big></big></big></big> | |||
''The origins of the Internet date back to the development of packet switching and research commissioned by the United States Department of Defense in the 1960s to enable time-sharing of computers. The primary precursor network, the ARPANET, initially served as a backbone for interconnection of regional academic and military networks in the 1970s. The funding of the National Science Foundation Network as a new backbone in the 1980s, as well as private funding for other commercial extensions, led to worldwide participation in the development of new networking technologies, and the merger of many networks. The linking of commercial networks and enterprises by the early 1990s marked the beginning of the transition to the modern Internet, and generated a sustained exponential growth as generations of institutional, personal, and mobile computers were connected to the network. Although the Internet was widely used by academia in the 1980s, commercialization incorporated its services and technologies into virtually every aspect of modern life.'' | |||
''The terms Internet and World Wide Web are often used interchangeably; it is common to speak of "going on the Internet" when using a web browser to view web pages. However, the World Wide Web or the Web is only one of a large number of Internet services, a collection of documents (web pages) and other web resources, linked by hyperlinks and URLs.'' | |||
* https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Internet | |||
: <big><big>World Wide Web</big></big> | |||
:: * http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/World_Wide_Web | |||
<big>[[World Wide Web]]</big> | |||
<big>[[Digital Rights]]</big> | |||
:::::[[File:Fact Checking @GreenPolicy360.jpg]] | :::::[[File:Fact Checking @GreenPolicy360.jpg]] | ||
Revision as of 22:16, 16 January 2022
<addthis />
Internet
The origins of the Internet date back to the development of packet switching and research commissioned by the United States Department of Defense in the 1960s to enable time-sharing of computers. The primary precursor network, the ARPANET, initially served as a backbone for interconnection of regional academic and military networks in the 1970s. The funding of the National Science Foundation Network as a new backbone in the 1980s, as well as private funding for other commercial extensions, led to worldwide participation in the development of new networking technologies, and the merger of many networks. The linking of commercial networks and enterprises by the early 1990s marked the beginning of the transition to the modern Internet, and generated a sustained exponential growth as generations of institutional, personal, and mobile computers were connected to the network. Although the Internet was widely used by academia in the 1980s, commercialization incorporated its services and technologies into virtually every aspect of modern life.
The terms Internet and World Wide Web are often used interchangeably; it is common to speak of "going on the Internet" when using a web browser to view web pages. However, the World Wide Web or the Web is only one of a large number of Internet services, a collection of documents (web pages) and other web resources, linked by hyperlinks and URLs.
- World Wide Web
Subcategories
This category has the following 25 subcategories, out of 25 total.
Pages in category "Internet"
The following 46 pages are in this category, out of 46 total.
D
E
G
M
Media in category "Internet"
The following 200 files are in this category, out of 213 total.
(previous page) (next page)- 33 false statements.png 640 × 91; 19 KB
- A Brief History of the Future - 2s.jpg 448 × 309; 70 KB
- A Planet Citizen View.png 799 × 1,241; 1.64 MB
- Above.png 500 × 375; 173 KB
- Acting to make a positive difference - in St Petersburg Florida.png 600 × 723; 645 KB
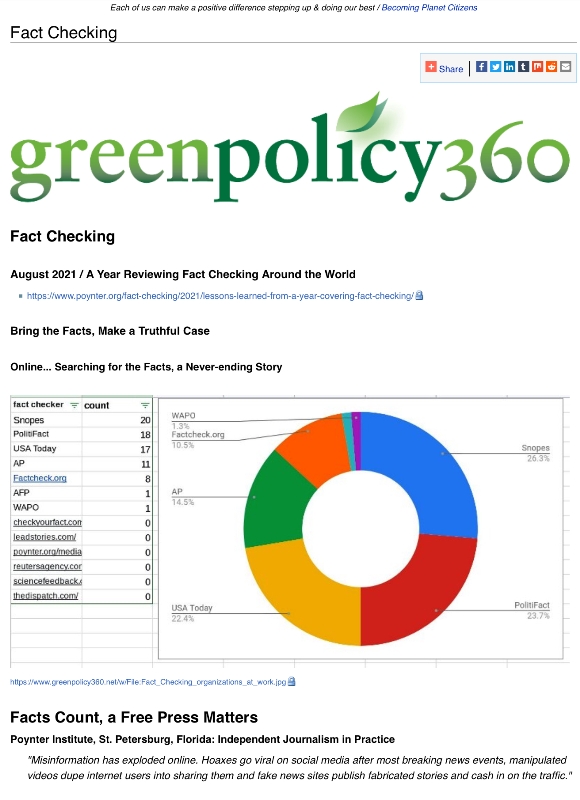
- American Jobs Act compared w THRIVE Act (Green New Deal).jpg 674 × 798; 90 KB
- Aspen Trees Fall Colors Web-of-Roots Connected Wiki commons.jpg 800 × 533; 171 KB
- Astro POV - Mike Massimino - PlanetCitizen.png 800 × 466; 792 KB
- Astro Samantha.png 448 × 266; 78 KB
- At Poynter, St Petersburg, Florida.png 640 × 345; 555 KB
- Attack from Within - by Barb McQuade.png 600 × 630; 222 KB
- Battle for Democracy.jpg 640 × 123; 24 KB
- Beginning of WWW 89 TimBerners-Lee CERN.jpg 522 × 753; 46 KB
- Biden-Harris, CNN News Online - Nov 8, 2020.jpg 800 × 484; 114 KB
- Biggest climate related legislation in history - 1.png 800 × 188; 68 KB
- Black Code, Inside the Battle for Cyberspace.jpg 224 × 346; 14 KB
- Blue Marble photo taken by the crew of Apollo 17 (1972).jpg 642 × 605; 129 KB
- Born-digital-generation.jpg 387 × 259; 95 KB
- Bucky Trimtab.jpg 348 × 336; 88 KB
- Canary - 1.jpg 448 × 901; 144 KB
- Canary - 2.png 446 × 531; 264 KB
- Carbon Footprint - BP-McKibben-Solnit-Aug2021.jpg 516 × 264; 66 KB
- ChatGPT talks of fighting climate denialism.png 707 × 747; 239 KB
- Citizen science and Climate change m.png 465 × 189; 19 KB
- Climate and National Security.jpg 603 × 533; 157 KB
- Climate Change in a Cloud.jpg 498 × 350; 152 KB
- Climate Change Poses a Widening Threat to National Security.png 600 × 781; 310 KB
- Computing and energy saving green solutions.jpg 521 × 476; 86 KB
- Connect cooperative networking 2.jpg 415 × 425; 48 KB
- Conversation prism.jpeg 561 × 600; 0 bytes
- ConversationPrism4 WEB 2880x1800.jpg 2,880 × 1,800; 981 KB
- Costs of War US Post 9-11 War Spending.jpg 800 × 305; 60 KB
- Countries Nations world map s.jpg 300 × 152; 16 KB
- Creative commons licenses.png 415 × 318; 31 KB
- Crew-1 over New Zealand.jpg 570 × 523; 86 KB
- Cyberlaw2.jpg 317 × 159; 18 KB
- Digital rights and responsibilities.jpg 438 × 163; 19 KB
- Digital Rights Tag Cloud from GreenPolicy360.net.png 814 × 459; 139 KB
- Digital.png 427 × 116; 51 KB
- Disinformation and Misinformation - via Wikipedia.jpg 800 × 69; 30 KB
- Donald Trump criminally charged in Miami, Florida - CNN.png 640 × 518; 589 KB
- Dove1 image.jpg 420 × 308; 26 KB
- Earth Day - DSCOVR-EPIC 2019.jpg 800 × 772; 150 KB
- Earth Day 2013 Google Doodle.png 458 × 225; 82 KB
- Earth Day 2022 - Act up.png 457 × 370; 155 KB
- Earth Day and Climate at the Center.jpg 595 × 604; 131 KB
- Earth Emoji.png 50 × 50; 2 KB
- Earth in Our Hands.png 76 × 76; 5 KB
- Earth Information Center - NASA 336.png 336 × 336; 279 KB
- Earth Information Center - NASA.png 768 × 769; 1.21 MB
- Earthrise - NASA - Astro Bill Anders.png 497 × 479; 216 KB
- Earths rotation as we roll thru space.jpg 800 × 529; 69 KB
- ElectionResources.png 607 × 243; 141 KB
- Electoral Reform US FairVote.jpg 662 × 270; 36 KB
- Emerging IT Map circa 2015.png 1,023 × 971; 555 KB
- EO Snapshot 6-29-2016 10-44-49 AM.png 839 × 768; 907 KB
- EOS starliner gr2.png 320 × 91; 3 KB
- EPA and the Green Bank - Feb 2023.png 476 × 542; 244 KB
- Fact Checking @GreenPolicy360.jpg 580 × 800; 206 KB
- FB IMG 1528669650732.jpg 1,261 × 960; 98 KB
- FOTN 2016 Censored Topics By Country-800x962.jpg 809 × 962; 276 KB
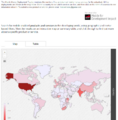
- FOTN 2016 World Internet Users-800x474.jpg 800 × 474; 155 KB
- FOTN 2016 WorldMap 484x316.jpg 484 × 316; 54 KB
- FOTN 2016 WorldMap 800x518.jpg 800 × 518; 107 KB
- Gavin Schmidt - NASA - January 2022.png 451 × 436; 150 KB
- Global Fossil CO2 Emissions 1960-2024.jpg 680 × 383; 30 KB
- Google Earth Engine.png 448 × 165; 45 KB
- Gov and money.jpg 240 × 210; 7 KB
- GP360 tagcloud2.png 655 × 400; 184 KB
- Green Best Practices 1.png 515 × 65; 5 KB
- Green Branching Out.jpg 400 × 194; 35 KB
- Green Networking @GreenPolicy360.net.png 788 × 604; 764 KB
- Green New Deal - Strategic Demands - Oct 1, 2021.png 602 × 658; 245 KB
- Green Wave.png 613 × 405; 427 KB
- GreenLinks logo - 2.png 451 × 84; 13 KB
- GreenLinks logo.png 644 × 120; 10 KB
- Greenpolicy360 logo 2med.png 493 × 88; 17 KB
- GrnPolicy360 bestpractice check aok.png 60 × 60; 2 KB
- GrnPolicy360.png 120 × 117; 26 KB
- Ground AI in Reality, a Renewable Energy case study.jpeg 495 × 640; 69 KB
- Hannah Arendt.jpg 527 × 680; 51 KB
- Human history, as an 800 page book.jpg 799 × 1,112; 148 KB
- Image3.png 196 × 30; 2 KB
- In Love with Earth.jpg 328 × 499; 15 KB
- International Fact-Checking Network - banner.png 800 × 384; 504 KB
- Internet Bill of Rights .png 281 × 23; 14 KB
- Internet Bill of Rights.png 469 × 38; 33 KB
- Internet Freedom - Democracy Status - FH Map 2022-23.png 800 × 407; 127 KB
- Internet future m.jpg 484 × 103; 20 KB
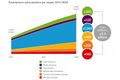
- Internet global growth 2015.png 500 × 375; 107 KB
- Internet map wikipedia.png 600 × 600; 691 KB
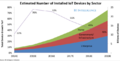
- Internet of Things estimates of growth.jpg 698 × 400; 35 KB
- Internet of Things industry sectors.png 698 × 345; 83 KB
- Internet Security.jpg 412 × 257; 26 KB
- Internet Trends 2018 Kleiner-Perkins by Mary Meeker.png 476 × 342; 28 KB
- Internet Users World-Region as of 2016.png 800 × 543; 131 KB
- Internet worldwide distribweb collab.jpg 830 × 592; 73 KB
- Internet+.jpg 728 × 567; 180 KB
- Intertidal Zone.png 800 × 474; 489 KB
- IoT-infographic.png 698 × 353; 80 KB
- IOTl multi-trillion-market.jpg 698 × 436; 45 KB
- Israel reacts to UN - Oct 25.jpg 631 × 707; 175 KB
- January 6 committee - on December 19 2022.png 640 × 468; 591 KB
- January 6 committee final hearing - news.png 600 × 661; 343 KB
- January 6 committee votes to issue criminal referrals against Trump.png 800 × 204; 458 KB
- Jigsaw Outline launch March 2018.png 633 × 565; 159 KB
- Joan and Christiana - April 2022.png 486 × 460; 282 KB
- Life of the Mind 2.png 300 × 245; 143 KB
- Loss of Privacy Downside to Rise of Personal Tech Jan2015.jpg 960 × 684; 156 KB
- M Channel Envisioning the Future 4.png 700 × 845; 246 KB
- Manchin again - July 15 2022.png 600 × 654; 523 KB
- Maria Ressa - Nobel Peace Prize speech.png 640 × 356; 283 KB
- Maria Ressa, Dmitry Muratov receive Nobel Peace Prize.jpg 700 × 600; 128 KB
- Mediawiki.png 120 × 136; 6 KB
- Mediawiki1.jpg 135 × 135; 6 KB
- Michael E Mann - July 2022.png 766 × 1,017; 671 KB
- Michael Mann, planet citizen.png 604 × 835; 273 KB
- Misinformation-Democracy-Hasen.png 496 × 480; 318 KB
- Mobile by 2020.png 498 × 67; 15 KB
- Mobile connections circa 2014.png 1,190 × 982; 380 KB
- Mobile Development Impact GSMA as of 2015.png 823 × 839; 269 KB
- Mobile subscriptions outnumber world population 2015.jpg 599 × 427; 37 KB
- Mobile world add-ons and replacements.png 303 × 352; 79 KB
- Mobile worldwide.jpg 583 × 482; 46 KB
- NASA and micro nano sats.png 443 × 431; 43 KB
- NASA Earth Science - Open Source Info.jpg 640 × 334; 60 KB
- NASA has a new mission... against Methane.png 800 × 576; 681 KB
- No incentives to tell the truth - social media misinfo era.png 640 × 364; 156 KB
- On the Beach, In the Intertidal Zone.png 448 × 263; 175 KB
- Open source initiative.jpg 259 × 194; 8 KB
- Oppenheimer, and the Doomsday Machine.png 703 × 830; 195 KB
- Over the Nile and Red Sea-2018.jpg 800 × 614; 49 KB
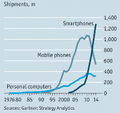
- PCs v Mobile phones v Smartphones 1970's-2015.png 216 × 203; 29 KB
- Piece of a Protoplanet.jpg 632 × 600; 69 KB
- Planet and plan for an Earthdata platform.png 600 × 600; 280 KB
- PlanetCitizen - Your Moment on Earth.jpg 650 × 625; 80 KB
- Planetcitizens.org (2).png 600 × 600; 550 KB
- Point of View of the Acceptance Speech.png 600 × 771; 687 KB
- President Biden - January 5, 2024.png 600 × 470; 236 KB
- President Biden speaks of protecting democracy - Jan 5 2024.png 600 × 686; 214 KB
- President Biden speaks of protecting democracy - News on Jan 5 2024.png 600 × 664; 351 KB
- Privacy rights in the digital age-published2016 s.jpg 173 × 225; 12 KB
- Privacy rights in the digital age-published2016.jpg 432 × 562; 54 KB
- Privacyrights toc.pdf ; 112 KB
- Profits of War - $14 Trillion - Read the Brown Univ-Watson Instit Report.PNG 800 × 1,002; 261 KB
- Project 2025 - Russell Vought and Donald Trump (AP).png 600 × 631; 453 KB
- Radio.garden.png 534 × 313; 244 KB
- Rebecca Google Outreach.jpg 276 × 183; 9 KB
- Remembering E.O. Wilson and Thomas Lovejoy.jpg 640 × 327; 56 KB
- RevDem.png 225 × 75; 5 KB
- Sagan - That's home.jpg 506 × 605; 54 KB
- Science on climate change.jpg 443 × 572; 125 KB
- Scrolling thru social media GreenLinks.png 600 × 365; 122 KB
- Smart phone usage global increase use percentage proj thru 2021.png 399 × 336; 128 KB
- Smartphone-user-chart-2014-2020.jpg 720 × 480; 54 KB
- Social-media-infowars.png 800 × 334; 49 KB
- Space stations - July 26 2022.png 544 × 462; 270 KB
- Speed and Scale Action Plan.png 550 × 867; 132 KB
- Speed and Scale Poster.png 490 × 772; 101 KB
- Starlink-nasa image.jpg 800 × 534; 127 KB
- Steven J Schmidt, May 2023.png 363 × 484; 383 KB
- Stopping the Steal, HBO documentary Sept 2024.png 600 × 683; 246 KB
- StratDem logo4.png 316 × 100; 10 KB
- Surprise climate deal.png 589 × 735; 83 KB
- Surviving Victory conf Sept20,2006.pdf ; 2.16 MB
- The Great Hack.jpg 640 × 395; 73 KB
- The Oath and the Office.png 572 × 480; 151 KB
- The Rainforest Canopy, the Richest Biosphere on Earth.png 745 × 757; 730 KB
- The rise of the internet.png 600 × 420; 100 KB
- Time for Facts and Science.jpg 144 × 604; 45 KB
- Time to Advance New Definitions of National Security.jpg 652 × 833; 104 KB
- Timelapse.png 800 × 566; 676 KB
- Tintin-hello world.png 600 × 417; 54 KB
- To be fully alive is to work for the common good.png 612 × 819; 621 KB
- To serve - from Chef José Andrés.png 600 × 798; 535 KB
- Tom Lovejoy on Biological Diversity.png 594 × 180; 48 KB
- Tom Lovejoy Planet Citizen.png 594 × 257; 25 KB
- Totalitarianism in the Age of Trump, Lessons from Hannah Arendt.png 638 × 644; 143 KB
- Trump on Termination of US Constitution - 1.jpg 600 × 607; 166 KB
- Trump on Termination of US Constitution - 2.jpg 600 × 600; 181 KB
- Trump on Termination of US Constitution - 3.PNG 600 × 600; 227 KB
- Trump opposing fact checking.jpeg 640 × 199; 24 KB
- Trump's campaign against facts & fact checking.jpeg 640 × 247; 41 KB
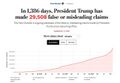
- Updated Nov 5 2020 - 29,508 false or misleading statements.jpg 640 × 444; 48 KB
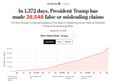
- Updated Oct 22 2020 - 26,548 false or misleading statements.jpg 640 × 444; 47 KB
- Virality, social media networking.png 640 × 406; 181 KB
- Vorsorgeprinzip at GreenPolicy360 - sjs.png 611 × 758; 164 KB