INDCs: Difference between revisions
Siterunner (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Siterunner (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
<big><big>'''''Climate Action Headline News'''''</big></big> | |||
<big>'''''Climate Action Headline News'''''</big> | |||
:''http://newsroom.unfccc.int/'' | :''http://newsroom.unfccc.int/'' | ||
Revision as of 15:52, 20 February 2017
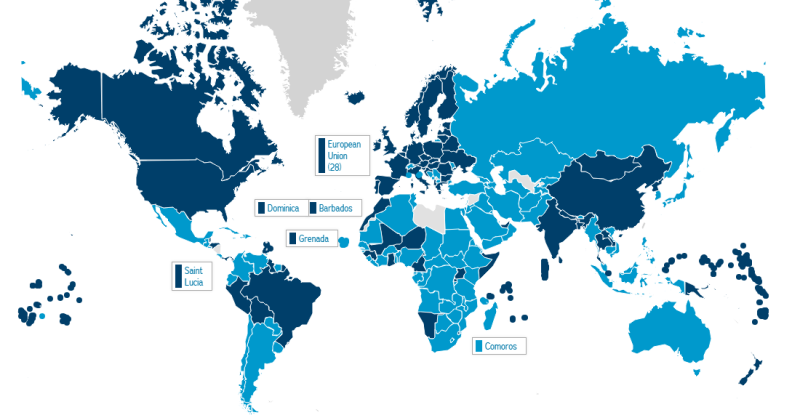
Click on the Map for the Latest Country-by-Country News
- European Union Votes to Ratify the #ParisAgreement
- The most comprehensive international agreement ever to combat man-made climate change will take effect in November, less than a year after negotiators from more than 190 countries reached international accord.
- October 5, 2016 / The European Parliament yesterday approved ratification of the Paris climate accord by the European Union (EU).
- United Nations Secretary-General Ban Ki-moon: "There are two requirements for the Paris Agreement to enter into force. Fifty-five parties to the Agreement, and fifty-five percent of greenhouse gas emissions accounted for... With the action taken by the EU Parliament, we will achieve both thresholds."
Climate Action Headline News
○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○
INDCs
Intended Nationally Determined Contributions / Individual Nation's Climate Plans
http://www.greenpolicy360.net/w/Category:INDC
http://www.greenpolicy360.net/w/Intended_Nationally_Determined_Contributions
○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○
Next Requirements
195 countries signed onto the new international climate agreement at COP21 in Paris.
Does that mean the Agreement is now in effect?
No, countries still need to take steps so that it takes effect. What occurred on December 12 at COP21 was the “adoption” of the Paris Agreement by the Conference of the Parties (COP) to the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). Adoption is the formal act that establishes the form and content of an agreement.
In addition to adopting the Paris Agreement, the Parties made a number of key decisions about what’s necessary for the Agreement to enter into force. They also agreed on a process for how countries will finalize their current national climate plans and shift them from being Intended Nationally Determined Contributions (INDCs) into Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs).
Countries must now actually join the Paris Agreement and become Parties to it. To do this, each country must now sign and indicate their consent to be bound by the Agreement.
After at least 55 Parties to the UNFCCC representing at least 55 percent of total global greenhouse gases sign on and indicate their consent to be bound will the Agreement “enter into force,” meaning it will come into effect and be legally binding.
After entry into force, the first meeting of the Parties to the Paris Agreement will be held. This will be an important time to adopt many of the more detailed rules and procedures necessary to make the Agreement effective.
What’s the timeline for countries to ratify the Agreement?
On April 22, 2016, all Heads of State can sign the Agreement at a high-level signing ceremony at the United Nations in New York.
The Agreement will then be open for signature for one year, until April 21, 2017.
Most countries will sign the Agreement “subject to ratification, acceptance and approval,” making their signature conditional on obtaining the required domestic approval for joining the Agreement. In some cases, they will also enact any national legislation necessary to implement the Agreement. For example, in Australia, the only requirement is formal notification and introduction of the Agreement in Parliament, whereas in Mexico, the consent of the Senate is also required. In the United States, many international agreements are joined as “executive agreements” based on presidential authority.
○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○
National Climate Plans - Countries
Submitted national plans as of December 2015 -- http://www4.unfccc.int/submissions/INDC/Submission%20Pages/submissions.aspx
INDC portal -- http://unfccc.int/focus/indc_portal/items/8766.php
○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○
Individual Plans / Social Media News
https://twitter.com/hashtag/INDCs?src=hash
○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○
VIA CLIMATE ACTION TRACKER
http://climateactiontracker.org/indcs.html
○ ○ ○ ○
VIA CLIMATE CHANGE NEWS
Paris tracker: Who pledged what for 2015 UN climate pact?
○ ○ ○ ○
VIA CLIMATE ENERGY / INDC FACTSHEETS
http://www.climate-energy-college.net/indc-factsheets
Comprehensive overview of submitted INDCs with quantification where possible.
In cooperation with the PRIMAP group at Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research.
○ ○ ○ ○
VIA the CENTER for CLIMATE and ENERGY SOLUTIONS / COMPARISON OF INDCS
http://www.c2es.org/international/2015-agreement/indcs
http://www.c2es.org/indc-comparison
○ ○ ○ ○
VIA NAMA NEWS / INDC CLIMATE ACTION PLANS
http://namanews.org/news/indc-tree/
http://namanews.org/news/about-namas/
○ ○ ○ ○
- Pages with broken file links
- INDC
- Anthropocene
- Atmosphere
- Atmospheric Science
- Biodiversity
- Citizen Science
- Agriculture
- Best Practices
- Carbon Sequestration
- City Governments
- Climate Change
- Climate Policy
- Countries
- Desertification
- Earth Observations
- Earth360
- Earth Science
- Ecological Economics
- Ecology Studies
- Environmental Full-cost Accounting
- Environmental Laws
- Environmental Protection
- Environmental Security
- Environmental Security, National Security
- Externalities
- Forests
- Globalization
- Green Energy Initiatives
- Green Best Practices
- Green Climate Fund
- Green Infrastructure
- Green Networking
- Green Politics
- Land Ethic
- Model Legislation
- Natural Resources
- NASA
- Networking
- Oceans
- Ocean Sustainability
- Permaculture
- Planet Citizen
- Rain Forest
- Renewable Energy
- Resilience
- Sea-Level Rise & Mitigation
- Smart Growth
- State
- Strategic Demands
- Sustainability Policies
- United Nations
- United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change
- Whole Earth