File:Racing Extinction websiteplankton.jpg: Difference between revisions
Siterunner (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Siterunner (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ | |||
'''LARGE "CHARISMATIC" SPECIES''' | '''LARGE "CHARISMATIC" SPECIES''' | ||
SJS / GP360 Siterunner: The standard approach, when looking at threatened species, is to focus on well-known larger species. The [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IUCN_Red_List '''Red List'''] is widely known for its work to identify species at risk of extinction | SJS / GP360 Siterunner: The standard approach, when looking at threatened species, is to focus on well-known larger species. The [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IUCN_Red_List '''Red List'''] is widely known for its work to identify species at risk of extinction. | ||
The large 'charismatic', or 'iconic' species, | The Red List [http://www.iucn.org/about/work/programmes/species/our_work/the_iucn_red_list/ is an essential reference] for many biodiversity preservation efforts. | ||
What many wildlife conservation campaigns focus on however are [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_world's_100_most_threatened_species larger, readily identified animals.] These species, often mammals, form just a part of the larger picture of our threatened environment. | |||
The large 'charismatic', or 'iconic' species, often foreclose recognition of rarely considered species that are not 'known' or known to be in danger... The reality is that much of the extinction in our era is of the small species, the lesser known, unknown and unconsidered species, whether in the rich biospheres of the rainforest or the oceans, the micro-organisms are at risk and in peril of collapse. | |||
When we speak of Plankton, as a profoundly critical keystone species, the food chain of the oceans begins with plankton, yet the disruption of the atmosphere and the heating of the ocean, or acidification, will have great consequences to the Phytoplankon, flagellates who cannot move with their limited locomotion system... Acidification of the oceans and the increases of heat or strengthened suns rays due to changes in atmospheric conditions and UV radiation can have deadly consequences to the 'least of and smallest of' the species -- and as a result effect the larger systems in ways that science is only now beginning to measure and monitor. | When we speak of Plankton, as a profoundly critical keystone species, the food chain of the oceans begins with plankton, yet the disruption of the atmosphere and the heating of the ocean, or acidification, will have great consequences to the Phytoplankon, flagellates who cannot move with their limited locomotion system... Acidification of the oceans and the increases of heat or strengthened suns rays due to changes in atmospheric conditions and UV radiation can have deadly consequences to the 'least of and smallest of' the species -- and as a result effect the larger systems in ways that science is only now beginning to measure and monitor. | ||
| Line 32: | Line 36: | ||
'''Visit [[Microbiomes at Risk]]''' | '''Visit [[Microbiomes at Risk]]''' | ||
'''Marine Biodiversity Strongly Linked to Ocean Temperature''' | '''Marine Biodiversity Strongly Linked to Ocean Temperature''' | ||
| Line 41: | Line 43: | ||
The researchers found striking similarities among the distribution patterns, with temperature strongly linked to biodiversity for all thirteen groups studied. These results imply that future changes in ocean temperature, such as those due to climate change, may greatly affect the distribution of life in the sea. | The researchers found striking similarities among the distribution patterns, with temperature strongly linked to biodiversity for all thirteen groups studied. These results imply that future changes in ocean temperature, such as those due to climate change, may greatly affect the distribution of life in the sea. | ||
http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2010/07/100728131707.htm | * http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2010/07/100728131707.htm | ||
<big><big>'''Plankton'''</big></big> | <big><big>'''Plankton'''</big></big> | ||
| Line 65: | Line 67: | ||
~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ | ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ | ||
<big>'''Tiny Blue Green'''</big> | <big>'''Tiny Blue Green'''</big> | ||
| Line 74: | Line 77: | ||
[[Category:Anthropocene]] | |||
[[Category:Atmospheric Science]] | |||
[[Category:Biodiversity]] | |||
[[Category:Climate Change]] | [[Category:Climate Change]] | ||
[[Category:Earth Observations]] | [[Category:Earth Observations]] | ||
| Line 87: | Line 93: | ||
[[Category:Oceans]] | [[Category:Oceans]] | ||
[[Category:Sustainability]] | [[Category:Sustainability]] | ||
[[Category:Whole Earth]] | |||
[[Category:Wildlife]] | |||
Revision as of 20:46, 8 October 2019
○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○
LARGE "CHARISMATIC" SPECIES
SJS / GP360 Siterunner: The standard approach, when looking at threatened species, is to focus on well-known larger species. The Red List is widely known for its work to identify species at risk of extinction.
The Red List is an essential reference for many biodiversity preservation efforts.
What many wildlife conservation campaigns focus on however are larger, readily identified animals. These species, often mammals, form just a part of the larger picture of our threatened environment.
The large 'charismatic', or 'iconic' species, often foreclose recognition of rarely considered species that are not 'known' or known to be in danger... The reality is that much of the extinction in our era is of the small species, the lesser known, unknown and unconsidered species, whether in the rich biospheres of the rainforest or the oceans, the micro-organisms are at risk and in peril of collapse.
When we speak of Plankton, as a profoundly critical keystone species, the food chain of the oceans begins with plankton, yet the disruption of the atmosphere and the heating of the ocean, or acidification, will have great consequences to the Phytoplankon, flagellates who cannot move with their limited locomotion system... Acidification of the oceans and the increases of heat or strengthened suns rays due to changes in atmospheric conditions and UV radiation can have deadly consequences to the 'least of and smallest of' the species -- and as a result effect the larger systems in ways that science is only now beginning to measure and monitor.
We are, our species is, beginning to understand that as the small animals comprising the foundations of the 'food chain' and biosphere systems are disrupted, endangered and/or destroyed, the rest of the food chain and integral ecological connections between species will be disrupted, endangered, and/or destroyed.
This is a great challenge of the era in which we live... loss of biodiversity and a 'ripple effect' over time, a threat environment that demands strategic environmental security as a key goal, as a policy objective beginning with awareness and policies and practices of sustainability.
○
SMALL v LARGE SPECIES
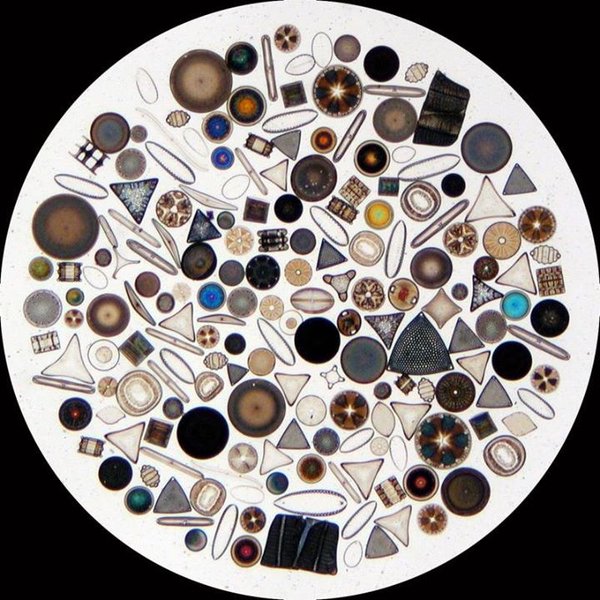
Phytoplankton obtain energy through the process of photosynthesis and must therefore live in the well-lit surface layer (termed the euphotic zone) of an ocean, sea, lake, or other water. Phytoplankton account for half of all photosynthetic activity on Earth...
Phytoplankton are responsible for much of the oxygen present in the Earth’s atmosphere – half of the total amount produced by all plant life.
Visit www.tinybluegreen.com to appreciate the immense impact of the tiny, unseen creatures and microscopic world's impact on life on Earth.
Visit Microbiomes at Risk
Marine Biodiversity Strongly Linked to Ocean Temperature
ScienceDaily / 2010 — In an unprecedented effort published online by the international journal Nature, a team of scientists mapped and analyzed global biodiversity patterns for over 11,000 marine species ranging from tiny plankton to sharks and whales.
The researchers found striking similarities among the distribution patterns, with temperature strongly linked to biodiversity for all thirteen groups studied. These results imply that future changes in ocean temperature, such as those due to climate change, may greatly affect the distribution of life in the sea.
Plankton
2015 - Big Trouble Ahead for Ocean Plankton
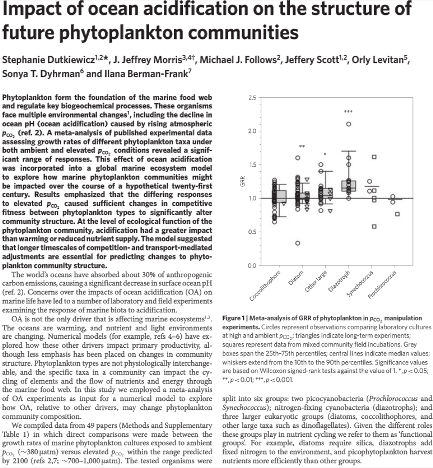
Sobering news: Ocean acidification will likely kill off some phytoplankton species and let others thrive, while warming waters will likely cause mass phytoplankton migrations toward the poles. In short: The base of the marine food web could be in for some serious upheaval in the coming decades. Here’s more from MIT News:
“I’ve always been a total believer in climate change, and I try not to be an alarmist, because it’s not good for anyone,” says (Dr. Stephanie) Dutkiewicz, who is the paper’s lead author. “But I was actually quite shocked by the results. The fact that there are so many different possible changes, that different phytoplankton respond differently, means there might be some quite traumatic changes in the communities over the course of the 21st century. A whole rearrangement of the communities means something to both the food web further up, but also for things like cycling of carbon.”
Dutkiewicz and her colleagues studied 154 published experiments ...
Phytoplankton ...
~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~
Tiny Blue Green
~
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 01:43, 10 November 2015 |  | 664 × 360 (141 KB) | Siterunner (talk | contribs) | www.racingextinction.com '''LARGE "CHARISMATIC" SPECIES''' GP360: The standard approach, when looking at threatened species, is to focus on well-known larger species. The [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IUCN_Red_List '''Red List'''] is widely known fo... |
You cannot overwrite this file.