Category:IOT
Internet of Things
A connected future...
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Internet_of_Things
The Internet of Things (IoT) is the network of physical objects—devices, vehicles, buildings and other items—embedded with electronics, software, sensors, and network connectivity that enables these objects to collect and exchange data.[1] The IoT allows objects to be sensed and controlled remotely across existing network infrastructure,[2] creating opportunities for more direct integration of the physical world into computer-based systems, and resulting in improved efficiency, accuracy and economic benefit;[3][4][5][6][7][8] when IoT is augmented with sensors and actuators, the technology becomes an instance of the more general class of cyber-physical systems, which also encompasses technologies such as smart grids, smart homes, intelligent transportation and smart cities. Each thing is uniquely identifiable through its embedded computing system but is able to interoperate within the existing Internet infrastructure. Experts estimate that the IoT will consist of almost 50 billion objects by 2020...
http://www.cisco.com/c/dam/en_us/about/ac79/docs/innov/IoT_IBSG_0411FINAL.pdf
April 2011 - Cisco Internet Business Solutions Group (IBSG) / White Paper
The Internet of Things: How the Next Evolution of the Internet Is Changing Everything
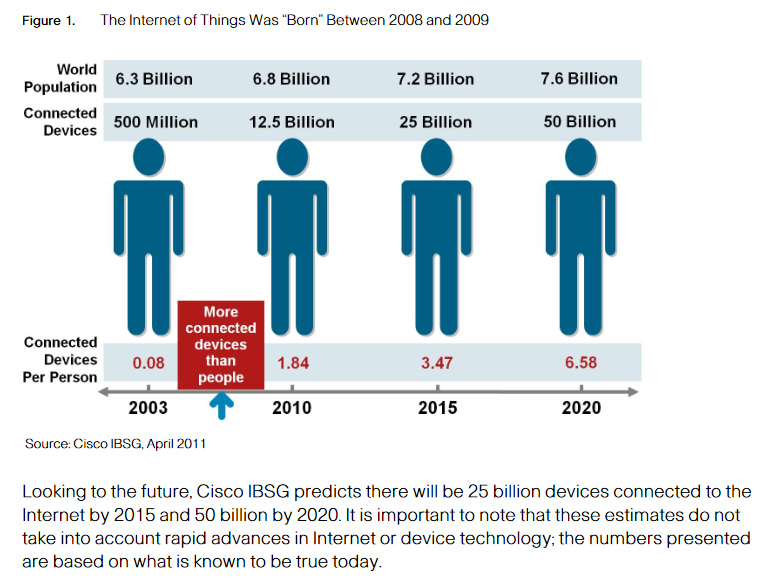
It is important to agree on a definition. According to the Cisco Internet Business Solutions Group, IoT is simply the point in time when more “things or objects” were connected to the Internet than people.
In 2003, there were approximately 6.3 billion people living on the planet and 500 million devices connected to the Internet.
By dividing the number of connected devices by the world population, we find that there was less than one (0.08) device for every person.
Based on Cisco's definition, IoT didn’t yet exist in 2003 because the number of connected things was relatively small given that ubiquitous devices such as smartphones were just being introduced. For example, Steve Jobs, Apple’s CEO, didn’t unveil the iPhone until January 9, 2007 at the Macworld conference.
Explosive growth of smartphones and tablet PCs brought the number of devices connected to the Internet to 12.5 billion in 2010, while the world’s human population increased to 6.8 billion, making the number of connected devices per person more than 1 (1.84 to be exact) for the first time in history.
Refining these numbers further, Cisco estimates the IoT was “born” sometime between 2008 and 2009 (see Figure 1).
Subcategories
This category has the following 2 subcategories, out of 2 total.
S
W
Pages in category "IOT"
The following 3 pages are in this category, out of 3 total.
Media in category "IOT"
The following 12 files are in this category, out of 12 total.
- Beginning of WWW 89 TimBerners-Lee CERN.jpg 522 × 753; 46 KB
- Born-digital-generation.jpg 387 × 259; 95 KB
- Internet map wikipedia.png 600 × 600; 691 KB
- Internet of Things estimates of growth.jpg 698 × 400; 35 KB
- Internet of Things industry sectors.png 698 × 345; 83 KB
- Internet worldwide distribweb collab.jpg 830 × 592; 73 KB
- IoT-infographic.png 698 × 353; 80 KB
- IOTl multi-trillion-market.jpg 698 × 436; 45 KB
- Smart home-energy-3d.png 703 × 356; 244 KB
- SmartHomeOntology.jpg 772 × 561; 154 KB
- Wordcloud.jpg 777 × 420; 60 KB
- Building Standards
- California
- Citizen Science
- City-County Governments
- Climate Policy
- Energy
- Energy Policy
- Green Best Practices
- IOT
- LEED
- Planet Citizen
- Planet Citizens, Planet Scientists
- Renewable Energy
- Smart Homes
- Solar Energy
- Sustainability Policies
- Climate Change
- Colleges
- Earth360
- EarthPOV
- Earth Science
- Ecology Studies
- Environmental Full-cost Accounting
- Environmental Protection
- Environmental Security
- EOS eco Operating System
- Externalities
- Green Politics
- Planet Scientist
- Planetary Science
- Policies
- Sea-level Rise
- Sea-Level Rise & Mitigation
- Sustainability
- Whole Earth