File:You are here on the cladogenetic tree m.jpg: Difference between revisions
Siterunner (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Siterunner (talk | contribs) (Evolution) |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
* https://www.flickr.com/photos/95447178@N06/15460245223 | * https://www.flickr.com/photos/95447178@N06/15460245223 | ||
* https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cladogenesis | |||
* https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anagenesis | |||
* https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phylogenetic_tree | |||
* https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phylogenetics | |||
'''[[It's All Related]]''' | |||
<big><big>Evolution</big></big> | |||
* https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Evolution | |||
''All life on Earth—including humanity—shares a last universal common ancestor (LUCA), which lived approximately 3.5–3.8 billion years ago. The fossil record includes a progression from early biogenic graphite to microbial mat fossils to fossilised multicellular organisms. Existing patterns of biodiversity have been shaped by repeated formations of new species (speciation), changes within species (anagenesis), and loss of species (extinction) throughout the evolutionary history of life on Earth. Morphological and biochemical traits are more similar among species that share a more recent common ancestor, and these traits can be used to reconstruct phylogenetic trees.'' | |||
http://www.greenpolicy360.net/mw/images/You_are_here_on_the_cladogenetic_tree.jpg | http://www.greenpolicy360.net/mw/images/You_are_here_on_the_cladogenetic_tree.jpg | ||
| Line 21: | Line 37: | ||
[[Category:Ecology Studies]] | [[Category:Ecology Studies]] | ||
[[Category:Environmental Protection]] | [[Category:Environmental Protection]] | ||
[[Category:Evolutionary Biology]] | |||
[[Category:Extinction]] | [[Category:Extinction]] | ||
[[Category:Green Graphics]] | [[Category:Green Graphics]] | ||
| Line 28: | Line 45: | ||
[[Category:Natural Resources]] | [[Category:Natural Resources]] | ||
[[Category:Open Access]] | [[Category:Open Access]] | ||
[[Category:Planet Citizens, Planet Scientists]] | |||
[[Category:Rights of Nature]] | [[Category:Rights of Nature]] | ||
[[Category:Seventh Generation Sustainability]] | [[Category:Seventh Generation Sustainability]] | ||
[[Category:Sustainability]] | [[Category:Sustainability]] | ||
Latest revision as of 19:10, 23 March 2023
Evolution
All life on Earth—including humanity—shares a last universal common ancestor (LUCA), which lived approximately 3.5–3.8 billion years ago. The fossil record includes a progression from early biogenic graphite to microbial mat fossils to fossilised multicellular organisms. Existing patterns of biodiversity have been shaped by repeated formations of new species (speciation), changes within species (anagenesis), and loss of species (extinction) throughout the evolutionary history of life on Earth. Morphological and biochemical traits are more similar among species that share a more recent common ancestor, and these traits can be used to reconstruct phylogenetic trees.
http://www.greenpolicy360.net/mw/images/You_are_here_on_the_cladogenetic_tree.jpg
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 15:41, 23 September 2015 | 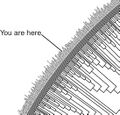 | 545 × 521 (73 KB) | Siterunner (talk | contribs) | http://www.greenpolicy360.net/w/Tree_of_Life Category:Biodiversity Category:Biogeosciences Category:Biosphere Category:Earth Science Category:Earth Law Category:Ecological Economics Category:Eco-Spirituality [[Category:Ecol... |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
- Biodiversity
- Biogeosciences
- Biosphere
- Earth Science
- Earth Law
- Ecological Economics
- Eco-Spirituality
- Ecology Studies
- Environmental Protection
- Evolutionary Biology
- Extinction
- Green Graphics
- Microbiology
- Microorganism
- Natural Capital
- Natural Resources
- Open Access
- Planet Citizens, Planet Scientists
- Rights of Nature
- Seventh Generation Sustainability
- Sustainability