File:Ecoregions of the World terrestrial-wiki.jpg: Difference between revisions
Siterunner (talk | contribs) (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ecoregion Category:Ecoregions) |
Siterunner (talk | contribs) (Siterunner uploaded a new version of "File:Ecoregions of the World terrestrial-wiki.jpg") |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ecoregion | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ecoregion | ||
http://www.greenpolicy360.net/w/Category:Ecoregions | |||
<big>'''Terrestrial Ecoregions of the World: A New Map of Life on Earth'''</big> | |||
http://wolfweb.unr.edu/~ldyer/classes/396/olsonetal.pdf | |||
November, 2001 - BioScience / The tapestry of life on Earth is unraveling as humans increasingly dominate and transform natural ecosystems. Scarce resources and dwindling time force conservationists to target their actions to stem the loss of biodiversity — a pragmatic approach, given the highly uneven distribution of species and threats (Soulé and Kohm 1989, Olson and Dinerstein 1998, Mace et al. 2000, Myers et al. 2000). Unfortunately, the ability to focus strategically is hindered by the absence of a global biodiversity map with sufficient biogeographic resolution to accurately reflect the complex distribution of the Earth’s natural communities. | |||
The above article with maps begins to address this need... | |||
We, GreenPolicy360, would add that humanity is still in the initial phases of discovery of life on Earth, terrestrial and oceans, in forest canopies and microbial soil. The 'tiny little ones' that go unseen and undiscovered, in every ecoregion and biosphere, are innumerable and, given the connectivity of life systems, essential to sustainability. | |||
Phytoplankton, the multitude of tiny creatures throughout oceans, the basis of the ocean food chain and in danger of climate change effects, account for half of all photosynthetic activity on Earth... [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phytoplankton Phytoplankton] are responsible for much of the oxygen present in the Earth’s atmosphere, half of the total amount produced by all plant life. Yet, like most all of the microbial life that enriches [http://www.greenpolicy360.net/w/Category:Soil soil and makes agriculture possible], the life in the sea goes unnoticed/undiscovered and for the greatest part unstudied as the [http://www.greenpolicy360.net/w/Extinction impacts from anthropogenic activities] escalate. | |||
Humans, homo sapiens on a [http://www.greenpolicy360.net/w/Tree_of_Life Tree of Life], are only now beginning to realize, much less discover and begin to protect and preserve, the extent of biodiversity in ecoregions. | |||
[[Category:Ecoregions]] | [[Category:Ecoregions]] | ||
[[Category:Biodiversity]] | |||
[[Category:Biosphere]] | |||
[[Category:Earth Science]] | |||
[[Category:Maps]] | |||
[[Category:Virtual Earth]] | |||
Latest revision as of 19:08, 14 April 2022
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ecoregion
http://www.greenpolicy360.net/w/Category:Ecoregions
Terrestrial Ecoregions of the World: A New Map of Life on Earth
http://wolfweb.unr.edu/~ldyer/classes/396/olsonetal.pdf
November, 2001 - BioScience / The tapestry of life on Earth is unraveling as humans increasingly dominate and transform natural ecosystems. Scarce resources and dwindling time force conservationists to target their actions to stem the loss of biodiversity — a pragmatic approach, given the highly uneven distribution of species and threats (Soulé and Kohm 1989, Olson and Dinerstein 1998, Mace et al. 2000, Myers et al. 2000). Unfortunately, the ability to focus strategically is hindered by the absence of a global biodiversity map with sufficient biogeographic resolution to accurately reflect the complex distribution of the Earth’s natural communities.
The above article with maps begins to address this need...
We, GreenPolicy360, would add that humanity is still in the initial phases of discovery of life on Earth, terrestrial and oceans, in forest canopies and microbial soil. The 'tiny little ones' that go unseen and undiscovered, in every ecoregion and biosphere, are innumerable and, given the connectivity of life systems, essential to sustainability.
Phytoplankton, the multitude of tiny creatures throughout oceans, the basis of the ocean food chain and in danger of climate change effects, account for half of all photosynthetic activity on Earth... Phytoplankton are responsible for much of the oxygen present in the Earth’s atmosphere, half of the total amount produced by all plant life. Yet, like most all of the microbial life that enriches soil and makes agriculture possible, the life in the sea goes unnoticed/undiscovered and for the greatest part unstudied as the impacts from anthropogenic activities escalate.
Humans, homo sapiens on a Tree of Life, are only now beginning to realize, much less discover and begin to protect and preserve, the extent of biodiversity in ecoregions.
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 19:08, 14 April 2022 |  | 800 × 400 (33 KB) | Siterunner (talk | contribs) | |
| 20:29, 31 January 2016 | 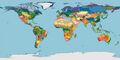 | 1,427 × 713 (85 KB) | Siterunner (talk | contribs) | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ecoregion Category:Ecoregions |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following 3 pages use this file: