New Space
In the early days of space flight and earth observations and science from space, the nation-states capable of aeronautic programs, launching and managing satellites were few. The United States and Russia's Soviet Union led the world in capabilities and programs in beginning in the 1950s.
In the 1960s and 1970s, a new generation of space-capable missions were launched, moving beyond military missions with a first generation of earth science/research from space. These programs developed the first remote imaging with digital instruments and data storage, sharing and applications.
After the U.S. space agency, NASA, was directed by Congress in the early 2000s to develop private-sector space partnerships and 'competition', in addition to the government space programs and their large costs of operation with a handful of corporate providers, a new era referred to as "New Space" rapidly began....
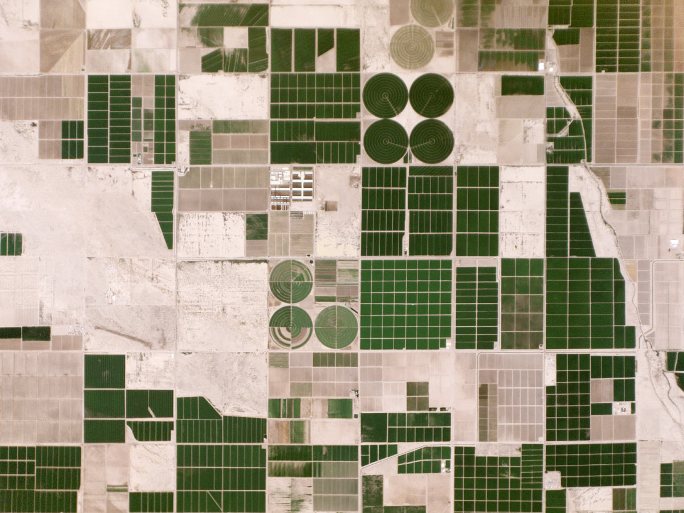
The small-satellite, New Space era is now powering up next generation remote imaging capabilities.
Start-up days with visions of atmospheric science/earth science/ocean science from space
Snapshots of today's New Space ventures
Planet Citizen Action
··············································································
New Space, Planet Citizen Science
- New ways to use OTS - off the shelf - micro-components
○
- Earth360
- EarthPOV
- Earth Imaging
- Earth Observations
- Overview Effect
- Biosphere
- Earth Law
- Earth Science
- Ecology Studies
- Environmental Full-cost Accounting
- Environmental Security
- Environmental Security, National Security
- EOS eco Operating System
- Externalities
- Land Ethic
- New Space
- Planet Citizens
- Planet Scientist
- Planet Citizens, Planet Scientists
- Sustainability
- Sustainability Policies
- ThinBlueLayer
- Whole Earth
- Atmospheric Science
- Biogeosciences
- Climate Change
- Cryosphere
- Geophysics and Geochemistry
- Mineralogy
- Geology
- Geophysics
- Hydrology
- Natural Resources
- Ocean Science
- Planetary Science
- Space Science and Space Physics