Category:Carbon Sequestration: Difference between revisions
Siterunner (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Siterunner (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carbon_sequestration | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carbon_sequestration | ||
https://www3.epa.gov/climatechange/ccs/#area | |||
Carbon Fixation | Carbon Fixation | ||
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carbon_fixation | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carbon_fixation | ||
<big><font color=green>'''○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○'''</font></big> | |||
Carbon dioxide (CO2) capture and sequestration (CCS) is a set of technologies that can greatly reduce CO2 emissions from new and existing coal- and gas-fired power plants and large industrial sources. CCS is a three-step process that includes: | |||
Capture of CO2 from power plants or industrial processes | |||
Transport of the captured and compressed CO2 (usually in pipelines). | |||
Underground injection and geologic sequestration (also referred to as storage) of the CO2 into deep underground rock formations. These formations are often a mile or more beneath the surface and consist of porous rock that holds the CO2. Overlying these formations are impermeable, non-porous layers of rock that trap the CO2 and prevent it from migrating upward. | |||
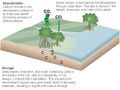
The figure below illustrates the general CCS process and shows a typical depth at which CO2 would be injected. Watch the following videos to learn more about how CCS works: | |||
* http://prod-mmedia.netl.doe.gov/Video/carbon_sequestration_animation.wmv | |||
* http://prod-mmedia.netl.doe.gov/Video/carbon_sequestration_sept.wmv | |||
○ | |||
Revision as of 16:06, 10 April 2016
Carbon Sequestration
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carbon_sequestration
https://www3.epa.gov/climatechange/ccs/#area
Carbon Fixation
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carbon_fixation
○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○
Carbon dioxide (CO2) capture and sequestration (CCS) is a set of technologies that can greatly reduce CO2 emissions from new and existing coal- and gas-fired power plants and large industrial sources. CCS is a three-step process that includes:
Capture of CO2 from power plants or industrial processes
Transport of the captured and compressed CO2 (usually in pipelines).
Underground injection and geologic sequestration (also referred to as storage) of the CO2 into deep underground rock formations. These formations are often a mile or more beneath the surface and consist of porous rock that holds the CO2. Overlying these formations are impermeable, non-porous layers of rock that trap the CO2 and prevent it from migrating upward.
The figure below illustrates the general CCS process and shows a typical depth at which CO2 would be injected. Watch the following videos to learn more about how CCS works:
- http://prod-mmedia.netl.doe.gov/Video/carbon_sequestration_animation.wmv
- http://prod-mmedia.netl.doe.gov/Video/carbon_sequestration_sept.wmv
○
Pages in category "Carbon Sequestration"
The following 9 pages are in this category, out of 9 total.
Media in category "Carbon Sequestration"
The following 35 files are in this category, out of 35 total.
- AOC March 26, 2019.jpg 597 × 433; 58 KB
- Biggest climate related legislation in history - 1.png 800 × 188; 68 KB
- Carbon cycle NOAA.jpg 640 × 480; 63 KB
- CarbonQuote Dr Rattan Lal.jpg 600 × 600; 542 KB
- Caroline Lucas-Green New Deal.jpg 584 × 391; 71 KB
- Climate Goals off course - 2018.png 800 × 556; 214 KB
- Common Ground, the Movie.png 600 × 756; 775 KB
- Disaster scenarios raise the stakes for Colorado River - 1.png 640 × 213; 56 KB
- Disaster scenarios raise the stakes for Colorado River - 2.png 640 × 154; 14 KB
- Don Perry SmithsonianCover.jpg 700 × 967; 873 KB
- Don Perry-credit-Roberta-Halsey.jpg 645 × 960; 114 KB
- Dr Volts talks of lawns and their problems.jpg 492 × 376; 49 KB
- EPA and the Green Bank - Feb 2023.png 476 × 542; 244 KB
- Farm du Bec Hellouin.jpg 800 × 480; 139 KB
- Gede Pangrango in the morning R.Martin CIFOR.jpg 800 × 532; 322 KB
- Green New Deal - Strategic Demands - Oct 1, 2021.png 602 × 658; 245 KB
- Hi, what are you doing up here Credit-Don Perry.jpg 391 × 576; 42 KB
- It's Time One day of NYC carbon emissions (2010) CarbonVisuals.jpg 900 × 599; 218 KB
- It's time to put a price on carbon 1 m.jpg 611 × 291; 53 KB
- Lawn1.jpg 1,024 × 431; 135 KB
- Manchin again - July 15 2022.png 600 × 654; 523 KB
- Permaculture-observation tip.jpg 480 × 540; 86 KB
- Pollution.jpg 720 × 480; 61 KB
- Regenerative Ag - Kiss the Ground - The Secret is in the Soil.png 800 × 800; 1.07 MB
- Soil Story AnnotatedScript 2015.pdf ; 391 KB
- Surprise climate deal.png 589 × 735; 83 KB
- Three trillion trees nature sept2015.jpg 946 × 800; 646 KB
- Three trillion trees.jpg 471 × 452; 26 KB
- Toxic sky ch.jpg 1,247 × 789; 49 KB