File:Planktonbluegreen tinyones.jpg
Planktonbluegreen_tinyones.jpg (640 × 320 pixels, file size: 99 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
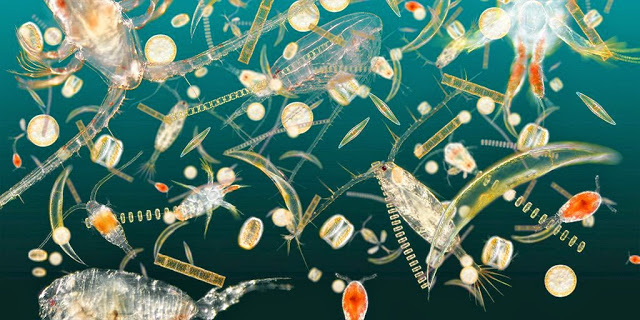
Types of Plankton
Plankton organisms include drifting or floating bacteria, archaea, algae, protozoa and animals that inhabit, for example, the pelagic zone of oceans, seas, or bodies of fresh water. Essentially, plankton are defined by their ecological niche rather than any phylogenetic or taxonomic classification...
○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○
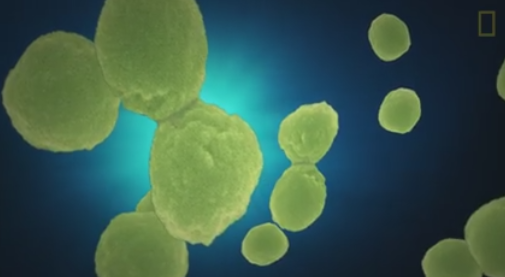
Oxygen production
Phytoplankton absorb energy from the Sun and nutrients from the water to produce their own food. In the process of photosynthesis, phytoplankton release molecular oxygen (O2) into the water.
It is estimated that between 50% — 85% of the world's oxygen is produced via phytoplankton photosynthesis. The rest is produced via photosynthesis on land by plants.
Phytoplankton photosynthesis controls atmospheric CO2/O2 balance.....
"A single kind of blue-green algae (Prochlorocossus) in the ocean produces the oxygen in one of every five breaths we take"
- Prochlorocossus
○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○
Phytoplankton
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phytoplankton
https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/da/Phytopla.jpg/220px-Phytopla.jpg
○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○
Zooplankton
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zooplankton
Differences between phytoplankton and zooplankton: Phytoplanktons are aquatic plants and produce energy. They have the capability to covert solar energy into chemical energy. Zooplanktons are sea animals and feed on phytoplankton and form the basis for the ocean food chain.
Estuaries and Plankton
Olivia Schmidt (April 2016): "I live next to an estuary..."
"This web page (pdf) says a lot about how a marine (ocean) food chain often starts with tiny blue-green life in estuaries." -- http://estuaries.noaa.gov/Teachers/pdf/Plankton_Food_Webs_VIMS.pdf
○
Plankton Food Webs
Estuarine and coastal marine food webs are dominated by plankton–organisms that drift with the currents.
Composed of phytoplankton - microscopic algae; zooplankton (above), animals that eat phytoplankton or each other; and bacterioplankton – microbes that degrade organic matter, plankton exist in an ever-changing aquatic environment that requires them to respond quickly to changes in their habitat on the time scales of days to weeks.
The plankton are thus often the first to be impacted by climate change.
○
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 20:28, 18 February 2016 |  | 640 × 320 (99 KB) | Siterunner (talk | contribs) | Category:Biodiversity Category:Citizen Science Category:Climate Change Category:Climate Policy Category:Earth Observations Category:Earth Science Category:Earth360 Category:Ecology Studies Category:Ecoregions [[Categ... |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
- Atmospheric Science
- Biodiversity
- Biogeosciences
- Citizen Science
- Climate Change
- Climate Policy
- Earth Observations
- Earth Science
- Earth360
- Ecology Studies
- Ecoregions
- Environmental Security
- Extinction
- Fisheries
- Green Graphics
- Microbiology
- Microorganism
- Oceans
- Ocean Ecosystem
- Ocean Science
- Ocean Sustainability
- Planet Citizen
- Planet Scientist
- Planet Citizens, Planet Scientists
- Whole Earth